Figure 3.
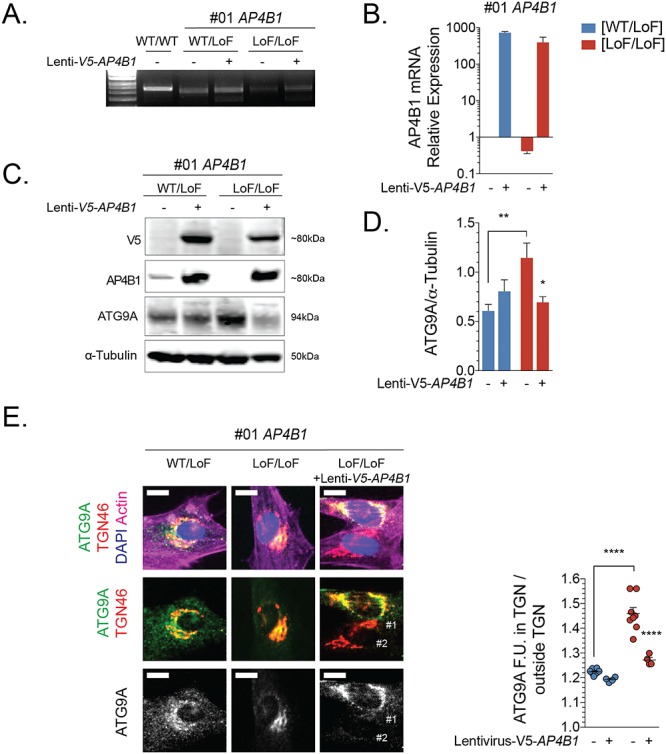
Re-expression of AP4B1 in fibroblasts from patients with AP4B1-associated HSP leads to a reduction of total ATG9A levels and redistribution from the trans-Golgi network to the cell periphery. (A, B) mRNA expression levels of AP4B1 in wild-type fibroblasts and fibroblasts with heterozygous or bi-allelic loss-of-function variants in AP4B1 with and without treatment with lentivirus to express human AP4B1. (C, D) Re-expression of AP4B1 in AP4B1-deficient patient-derived fibroblasts lowers ATG9A protein levels to levels that are not different from controls. (E) Re-expression of AP4B1 in AP4B1-deficient patient-derived fibroblasts leads to re-distribution of ATG9A from the trans-Golgi network to the cell periphery. Quantification of the area of ATG9A staining overlapping with TGN46 as a ratio to the total area of ATG9A staining demonstrates that the pattern after re-expression of AP4B1 is not significantly different from the pattern in heterozygous controls. Scale bar: 5 μm. Lenti, lentivirus; LoF, loss of function; TGN, trans-Golgi network; WT, wild type.
