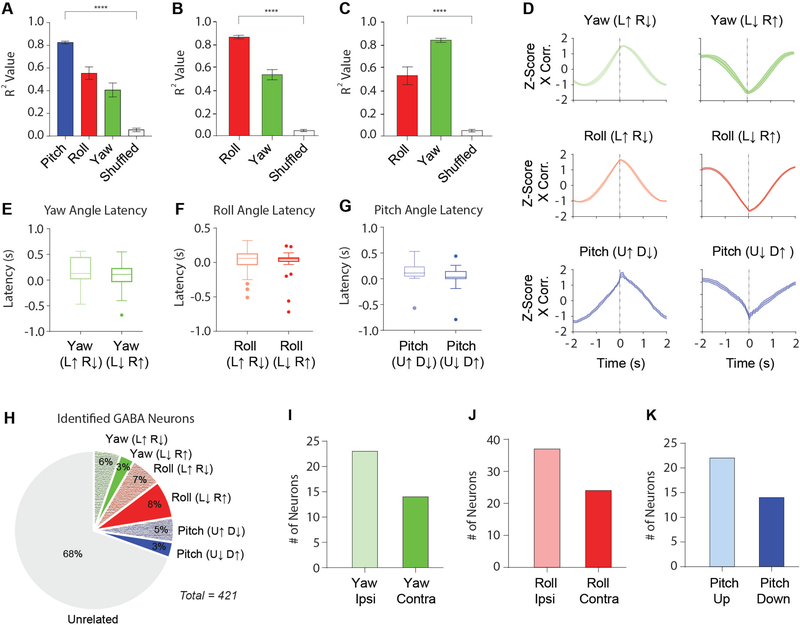
Figure 4. Summary of classified VTA GABAergic neurons.
(A) Average r2 values for yaw, roll, and pitch, as well as shuffled data from a Pearson Correlation (PC) analysis for neurons classified as pitch. (Pitch: r2 = 0.83 ± 0.01; Roll: r2 = 0.56 ± 0.03; Yaw: r2 = 0.41 ± 0.05; Mean ± SEM). Correlation with pitch angle is significantly higher than correlation with roll and yaw angles (One-way ANOVA: F(3,134) = 62.64, p < 0.0001; p values were corrected with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. **** p < 0.0001).
(B-C) Because yaw and roll co-varied during horizontal tracking and had similar r2 values when compared to the pitch population, we directly compared r2 values between roll and yaw angle along with shuffled data for neurons classified as yaw or roll angle neurons.
(B) There is a significant difference between the r2 values of yaw and roll angle for neurons categorized as roll neurons (One-way ANOVA, F(2,195) = 60.31, p < 0.0001, Roll: r2 = 0.87 ± 0.01; Yaw: r2 = 0.54 ± 0.03; Mean ± SEM).
(C) There is also a significant difference between the r2 values of yaw and roll angle for neurons categorized as yaw neurons (One-way ANOVA, F(2,90) = 37.36, p < 0.0001, Yaw: r2 = 0.83 ± 0.01; Roll: r2 = 0.54 ± 0.05; Mean ± SEM).
(D) Normalized cross-correlations for yaw neurons (top), roll neurons (middle), and pitch neurons (bottom). Latency between neural activity and behavior were determined from cross-correlation analysis.
(E) Latency between neural activity and yaw angle for both Yaw (L↑ R↓; = 180 ± 0.05 ms) and Yaw (L↓ R↑; = 52 ± 0.09 ms; Mean ± SEM) neurons.
(F) Latency between neural activity and roll angle for both Roll (L↑ R↓; = 60 ± 0.03 ms) and Roll (L↓ R↑; ( = 50 ± 0.03 ms; Mean ± SEM) neurons.
(G) Latency between neural activity and pitch angle for both Pitch (U↑ D↓; = 130 ± 0.04 ms) and Pitch (U↓ D↑; = 20 ± 0.07 ms; Mean ± SEM) neurons.
(H) Proportion of head angle neurons among all classified VTA GABAergic neurons.
(I) Number of yaw angle neurons that increase their firing rate in the ipsiversive direction (n = 23) or contraversive direction (n = 14) in relation to the recording hemisphere.
(J) Number of roll angle neurons that increase their firing rate in the ipsiversive direction (n = 37) or contraversive direction (n = 24) in relation to the recording hemisphere.
(K) Number of pitch angle neurons that increase their firing rate in the upward direction (n = 22) or downward direction (n = 14). See also Figure S4 and Videos S4 and S5.