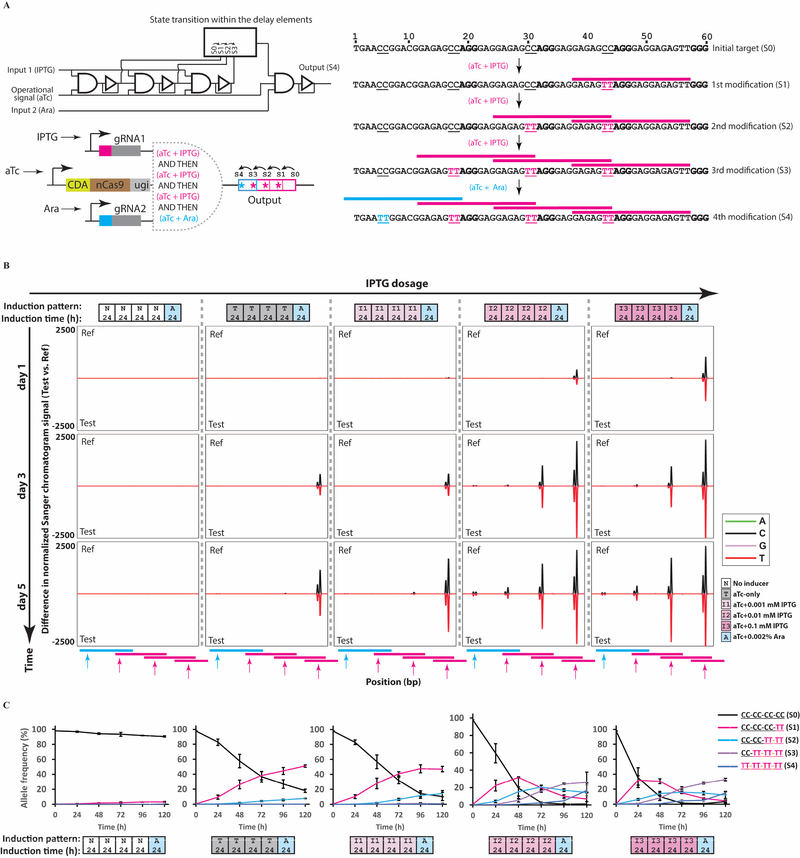
Figure 4 |. Incorporating propagation delay and temporal logic into living cells.
A) A schematic of a temporal AND gate built by overlapping DOMINO operators, for which the timing between the two signals is important to execute the AND function (see text for details). B) E. coli cells harboring the circuit shown in (A) were exposed to different concentrations of the first inducer (IPTG) for 4 days with serial dilution after each day, followed by a one-day exposure to the second inducer (Ara). The propagation of the signal as manifested by sequential mutations in the repeat array was monitored by analyzing Sanger chromatograms with Sequalizer. C) Transitions between the memory states for samples shown in (B) assessed by HTS. Error bars indicate standard deviation for three biological replicates. See also Figure S5.