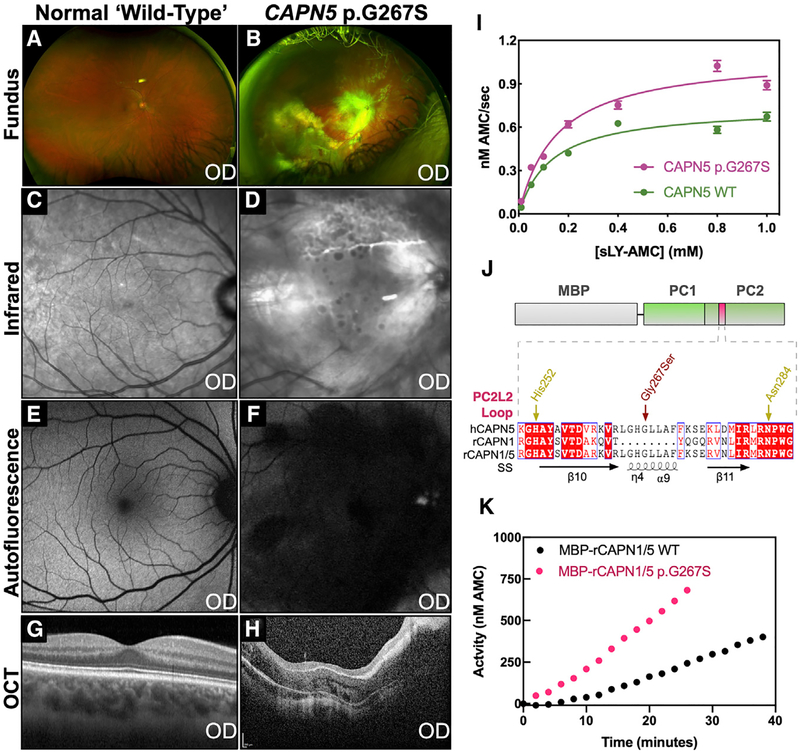
Figure 6. The Unique CAPN5 PC2L2 Loop Remotely Regulates Calpain Activity.
Clinical features of a NIV patient harboring a p.G267S mutation.
(A) Fundus image of the normal retina.
(B) Fundus image of the affected patient showing severe vasoproliferative vitreoretinal pathology.
(C) Infrared image of the normal retina.
(D) Infrared image of the affected patient showing sub-retinal exudate.
(E) Fluorescein angiogram of the normal retina.
(F) Fluorescein angiography of the affected patient reveals central retinal degeneration.
(G) Optical coherence tomography (OCT) of the normal retina.
(H) OCT of the affected patient reveals gross disturbance of normal retinal morphology secondary to unusual retinal nerve fiber layer myelination and fibrosis.
(I) Michaelis-Menten analysis of sLY-AMC hydrolysis by 10 μM WT and p.G267S CAPN5-PC in the presence of 10 mM Ca2+ (R2 = 0.96 and 0.96 for WT and p.G267S, respectively). Data are displayed as mean ± SEM (n = 3).
(J) Schematic representation of hybrid calpain constructs. Alignment of the PC2L2 loop region between human CAPN5, rat CAPN1, and the rat CAPN1/5 hybrid is represented below. SS denotes secondary structure annotations corresponding to CAPN5-PC.
(K) Hydrolysis of 0.2 mM sLY-AMC by 10 μM MBP-rCAPN1/5 (WT and p.G267S) in the presence of 10 mM Ca2+.