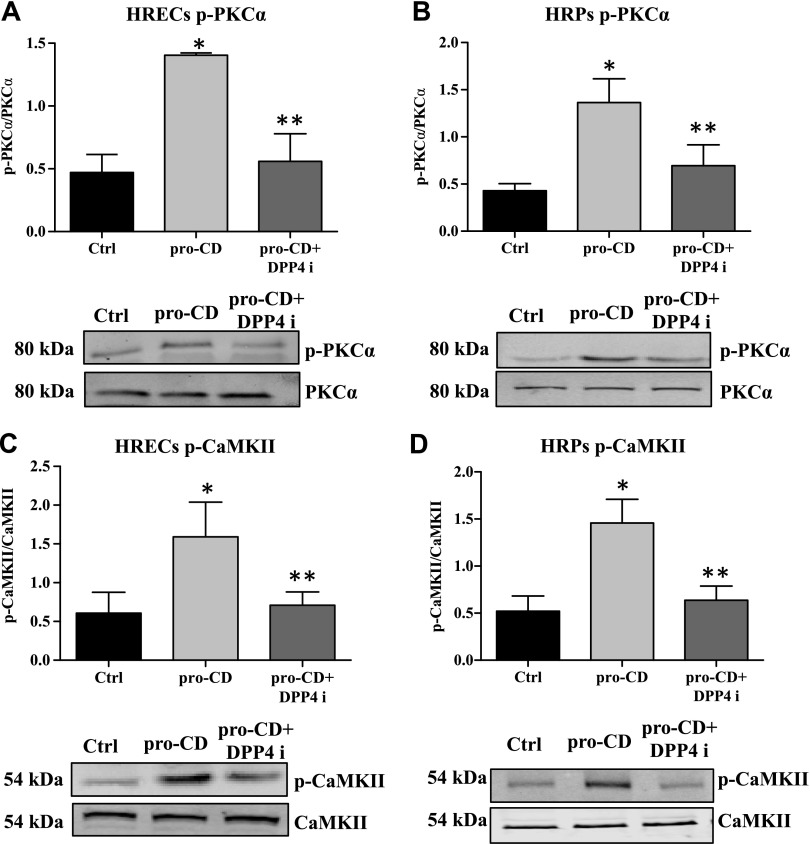
Figure 4.
Dephosphorylation of PKC-α/CaMKII by DPP4 inhibitor (DPP4i). Phosphorylation status of PKC-α/CaMKII in HRECs and HRPs as measured by Western blot. A) The phosphorylation level of PKC-α is significantly higher in pro-CD–treated HRECs compared with untreated cells. Pro-CD + DPP4i–treated cells have a significantly reduced phosphorylation form of PKC-α compared with pro-CD alone. *P = 0.003, **P = 0.01. B) In HRPs, the level of phosphor-PKC-α is significantly higher in pro-CD–treated cells compared with untreated cells. DPP4i treatment significantly reduced the level of phospho-PKC-α compared with pro-CD alone. *P = 0.007, **P = 0.05. C) The phosphorylation level of CaMKII is significantly higher in pro-CD–treated HRECs compared with untreated cells. Pro-CD + DPP4i cells have significantly reduced phospho-CaMKII compared with pro-CD alone. *P = 0.03, **P = 0.03. D) In HRPs, the level of phospho-CaMKII is significantly higher in pro-CD–treated cells compared with untreated cells. *P = 0.03. DPP4i treatment significantly reduced the level of phospho-CaMKII compared with pro-CD alone. Representative Western blots of total and phosphorylation forms of the proteins are placed at the bottom of the respective graphs. Data are presented as means ± sd. **P = 0.05.