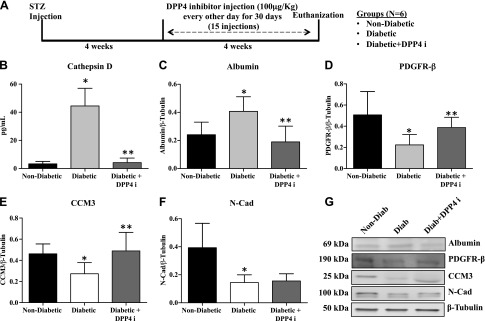
Figure 5.
DPP4 inhibitor (DPP4i) treatment reduces the increased permeability of retinal vasculature in diabetic rats. All protein levels were measured in the retinas of nondiabetic, diabetic rats, and diabetic rats that were treated with DPP4i. A) In vivo study design, timeline, and groups. B) CD levels as measured by ELISA showed a significant increase in retinas of diabetic rats compared with nondiabetic rats. DPP4i–treated diabetic rats had significantly less CD compared with diabetic rats. **P = 0.0003. C) Albumin levels as measured by Western blot to assess retinal vascular permeability demonstrated a significant increase in diabetic rats compared with nondiabetic rats. Drug treatment significantly reduced the albumin levels compared with untreated diabetic animals. *P = 0.02, **P = 0.01. D) PDGFRβ levels were significantly reduced in diabetic rats compared with nondiabetic rats. PDGFRβ levels were significantly increased in DPP4i–treated rats compared with untreated diabetic rats. *P = 0.01, **P = 0.05. E) CCM3 level is significantly reduced in the diabetic rats compared with the nondiabetic rats (*P = 0.02). CCM3 levels were significantly improved with drug treatment. **P = 0.05. F) The protein level of N-Cad was significantly reduced in diabetic animals compared with nondiabetic animals. There was no significant change in N-Cad expression in drug-treated animals compared with diabetic animals. *P = 0.009. G) Representative Western blot images of respective proteins. Data are presented as means ± sd (n = 6 in each group).