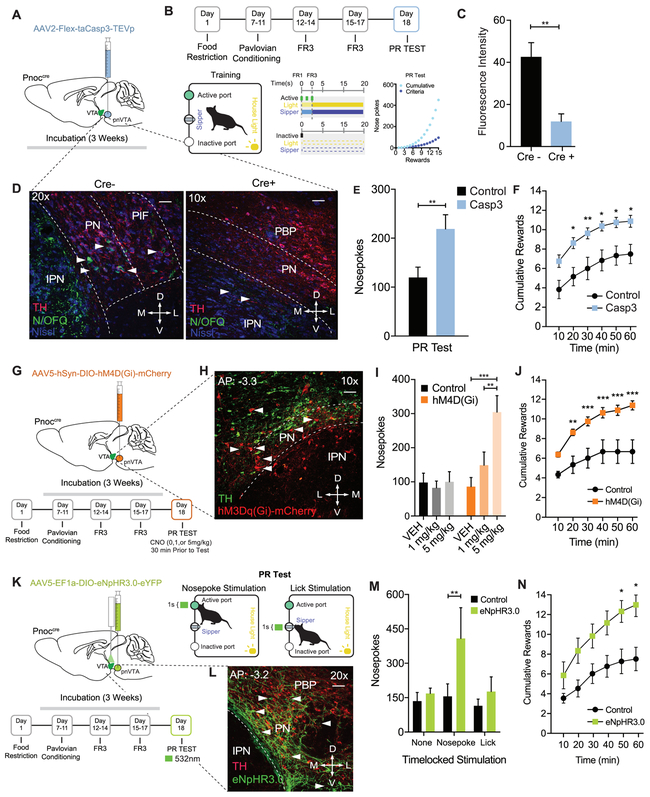
Figure 5: Selective Ablation and Inhibition of pnVTAPnoc Neurons Enhances Operant Responding for Natural Rewards.
(A) Cartoon depicting injection of AAV2-FLEX-taCasp3-TEVp into the pnVTA of Pnoc-Cre+ and Pnoc-Cre− mice.
(B) Schematic and timeline for the operant training schedule, FR, and PR test days.
(C) Quantification of fluorescence intensity from immunohistochemistry analysis for N/OFQ fluorescence in Pnoc-Cre+ and Pnoc-Cre− mice following cell ablation).
(D) Representative coronal images of the VTA and IPN showing immunohistochemistry for nociceptin (N/OFQ) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) staining in Pnoc-Cre− (left panel) and Pnoc-Cre+ (right panel) mice. Images show N/OFQ (green), DAPI (blue) and TH (red). Scale bars are 50 and 100μm, respectively.
(E) Nosepokes performed during PR test. Pnoc-CretaCasp3 mice have significantly increased nosepokes and rewards, compared to controls (n = 11 to 13: two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc; Nosepokes for control versus Casp3 during PR test **p < 0.01,.
(F) Cumulative rewards received in Control and Pnoc-CretaCasp3 mice. Pnoc-CretaCasp3 mice show significantly increased number of rewards received, compared to controls (n = 11 to 13: two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc; Nosepokes for Control versus Casp3 during PR test *p < 0.05, **p<0.01.
(G) Calendar for injection of AAV5-hSyn-DIO-hM4D(Gi)-mCherry into the pnVTA of Pnoc-Cre+ and Pnoc-Cre− mice. Schematic and timeline for the operant training schedule and FR and PR test days.
(H) Coronal images of the pnVTA and IPN showing immunofluorescence staining tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and hM4D(Gi)-mCherry following viral injection in Pnoc-Cre+ mice. Images show TH (green) and hM4D(Gi)-mCherry (red).
(I) Number of nosepokes performed during PR test. Pnoc-CrehM4D(Gi) mice show significantly increased active nosepokes compared to Controls (n = 8: two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc; Nosepokes for Vehicle versus 5mg/kg, ***p < 0.001, 1mg/kg versus 5mg/kg **p < 0.01.
(J) Cumulative rewards received in Control and Pnoc-CrehM4D(Gi) mice. Pnoc-CrehM4D(Gi) mice receive significantly more rewards over session, compared to controls (n = 8: two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc; Nosepokes for control versus hM4D(Gi) during PR test, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
(K) Calendar for injection of AAV5- EF1α-DIO-eNpHR3.0-eYFP into the pnVTA of Pnoc-Cre+ and Pnoc-Cre− mice. Schematic and timeline for the operant training schedule, FR and PR test days.
(L) Coronal images of pnVTA immunofluorescence staining of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and eNpHR3.0-eYFP following viral injection in Pnoc-Cre+ mice. Images show TH (red) and eNpHR3.0-eYFP (green).
(M) Number of nosepokes performed during PR test. Pnoc-CreeNpHR3.0 mice show significantly increased active nosepokes compared to Controls following nosepoke-paired inhibition (n = 6: two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc; **p<0.01)
(N) Cumulative rewards received in Control and Pnoc-CreeNpHR3.0 mice. Pnoc-CreeNpHR3.0 mice receive significantly more rewards over session compared to control mice following nosepoke-paired inhibition (n = 6: two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc; Nosepoke-paired inhibition Rewards for Control versus Pnoc-CreeNpHR3 during PR test, *p<0.05.