Figure 4. PBP1b localizes depending on the need for peptidoglycan synthesis.
(A-C) Calculated bound fraction of PBP1b at different levels of PBP1b, PBP1a and LpoB, using strains AV44, AV51 (ΔPBP1a) or AV110 (ΔLpoB). For GFP-PBP1b, sgRNA G14 (in pAV20), crRNA G10 (in pCRRNAcos) and crRNA GØ (in pCRRNAcos) are used to reach 30%, 130% and 370%, respectively. For RFP-PBP1a, sgRNA R20 (in pAV20), crRNA R18 (in pCRRNAcos) and crRNA RØ (in pCRRNAcos) are used to reach 20%, 280% and 1300%, respectively. Each point represents a biological replicate comprising at least 5000 tracks. Horizontal lines are means. p-Values are from permutation tests. (D-E) Bound fraction of PBP1b at different times during 1 mM D-cycloserine treatment (D) and during recovery from 30 min of D-cycloserine treatment (E) in the strain AV51/pCRRNAcos G10-RØ. Colored points are individual movies and white points are medians from one sample. Corresponding free diffusion coefficients are shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 4.
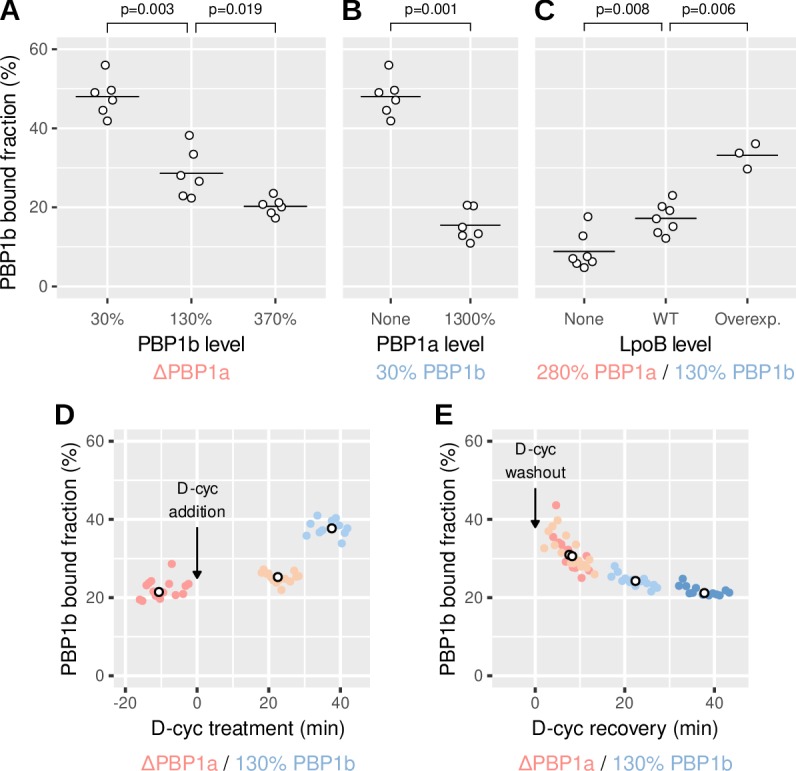
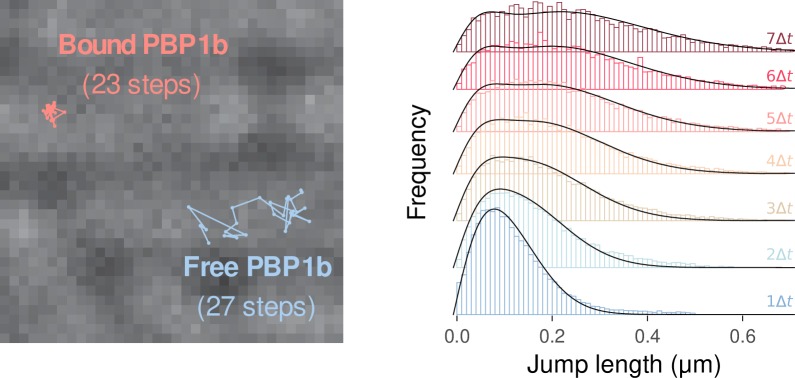
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Tracking of single molecules and quantification of the fraction of bound molecules.
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Localization of bound molecules.
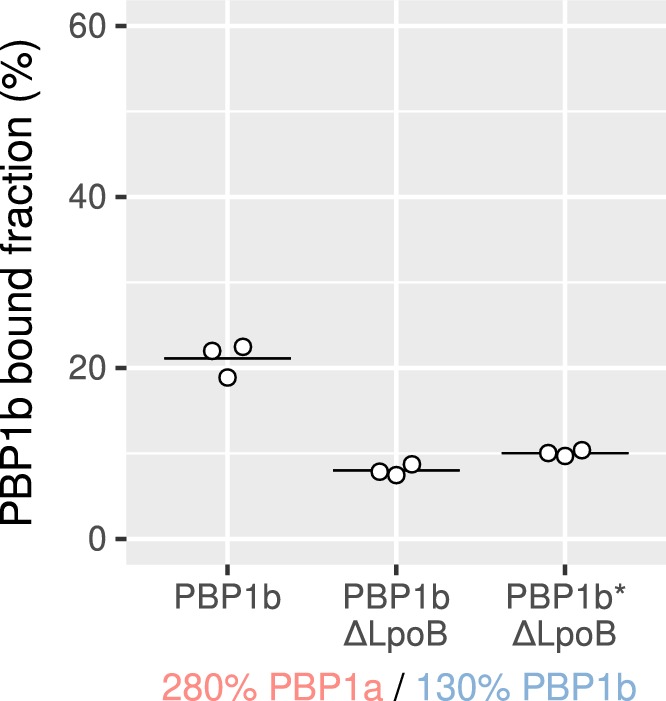
Figure 4—figure supplement 3. Calculated bound fraction of the PBP1b* mutant, compared to PBP1b with and without LpoB.