FIG 3.
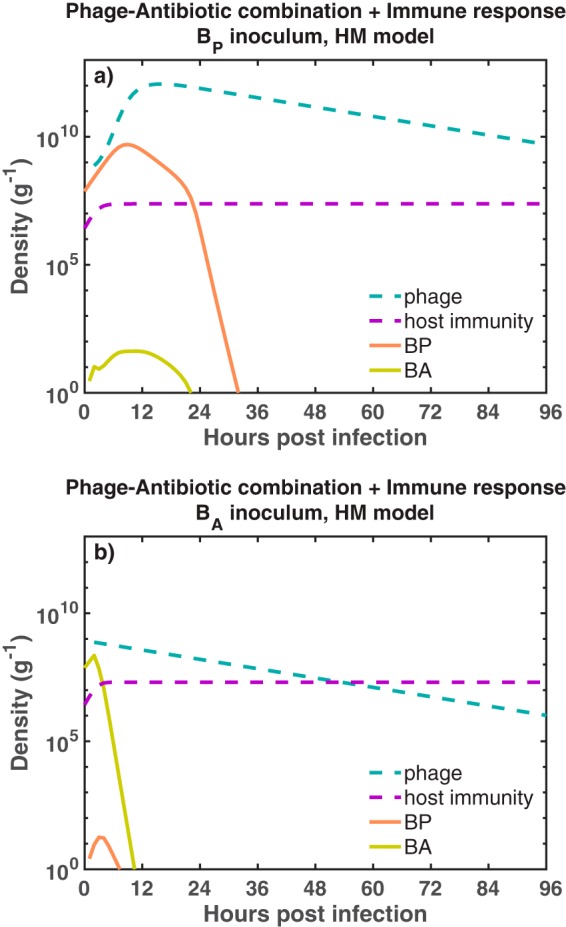
Outcomes of the phage-antibiotic combination therapy model for two different infection settings. We simulate the combined effects of phage and antibiotics in an immunocompetent host infected with phage-sensitive bacteria (a), BP (orange solid line). In panel b, the host is infected with antibiotic-sensitive bacteria, BA (green solid line). The dynamics of the phage (blue dashed line) and innate immunity (purple dashed line) are shown for each infection setting. Initial bacterial density and phage density are B0 = 7.4 × 107 CFU/g and P0 = 7.4 × 108 PFU/g, respectively. For the simulation, we use a heterogeneous mixing model as a functional form of phage infection. The simulation run is 96 h (4 days). Antibiotic and phage are administered 2 h after the beginning infection. Ciprofloxacin is maintained at a constant concentration of 0.0350 μg/ml during the simulation. The carrying capacity of the bacteria is KC = 1010 CFU/g.
