Fig. 4. Decreased brain serine and restored social behavior by acute DCS treatment in 15q dup mice.
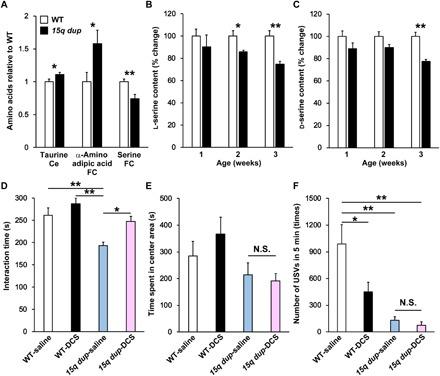
(A) Changes in amino acid concentrations between WT and 15q dup mice (n = 6 in each group). The mean level of WT-saline was set to 1. Ce, cerebellum; FC, frontal cortex. (B and C) Quantification of l- and d-serine concentrations in the frontal cortex. Mice that were 1 to 3 weeks postnatal were used for this analysis (n = 4, 7, and 10 15q dup and n = 9, 6, and 7 WT mice of ages 1, 2, and 3 weeks, respectively). The mean level for WT was set to 100%. Values are expressed with means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 significantly different from WT mice by Student’s t test. (D) Reciprocal social interaction test after administration of DCS or saline (WT-saline, n = 11; WT-DCS, n = 11; 15q dup-saline, n = 10; 15q dup-DCS, n = 12). (E) Novelty-induced anxiety in open-field test after administration of DCS or saline (WT-saline, n = 8; WT-DCS, n = 9; 15q dup-saline, n = 9; 15q dup-DCS, n = 10). (F) Adult USV calls after administration of DCS or saline (WT-saline, n = 8; WT-DCS, n = 9; 15q dup-saline, n = 9; 15q dup-DCS, n = 10). Values are expressed with means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; N.S., not significant following Tukey-Kramer procedure.
