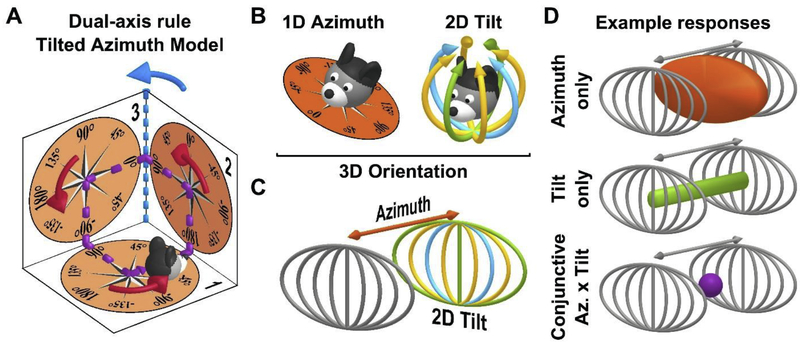
Figure 4: HDC encode head orientation in 3D.
A: Dual-axis rule and tilted azimuth model. Azimuth is measured on a compass (orange; tilted azimuth compass) affixed to the locomotion plane. Based on the dual-axis rule, azimuth is updated (1) when rotating on the locomotion plane (red arrows) and (2) when the plane rotates about an earth-vertical axis (blue; e.g. azimuth changes from 90° to 180° when moving from surface n°2 to surface n°3 along the violet trajectory). This rule ensures that azimuth maintains spatial invariance. For instance, when completing the trajectory shown in violet, the dual-axis rule registers a total rotation of 360° (three red turns and one blue turn). If only red turns updated the attractor, there would be a discrepancy with the allocentric environment.
B: Decomposition of 3D head orientation into 1D azimuth (left) and 2D tilt (right). Head tilt is two-dimensional, e.g. it can occur along the pitch (green), roll (blue) or intermediate (yellow) axes, and has a spherical topology since 180° tilt in any direction results in the same final position (upside-down).
C: Three-dimensional head orientation space, represented as the cartesian product of 1D azimuth and 2D tilt. The spherical 2D tilt space is projected onto a plane (using an equal-area Mollweide projection). An azimuth axis is added, orthogonal to this plane, to create a 3D space.
D: Representation of the response space of HDC responses with various degrees of dimensionality, in the 3D orientation space. Top: a HDC that encodes only azimuth will respond when the head faces a certain azimuth, and at any head orientation. The corresponding volume (orange) forms a vertical slice in the 3D space. Middle: a HDC that encodes only tilt will discharge around a certain tilt position (e.g. 90° pitch here) but at all possible azimuth angles. The corresponding volume (green) forms a line parallel to the azimuth axis. Bottom: a conjunctive HDC will discharge when the head reaches a specific range of tilt and azimuth, i.e. in the neighborhood of a single point (violet).