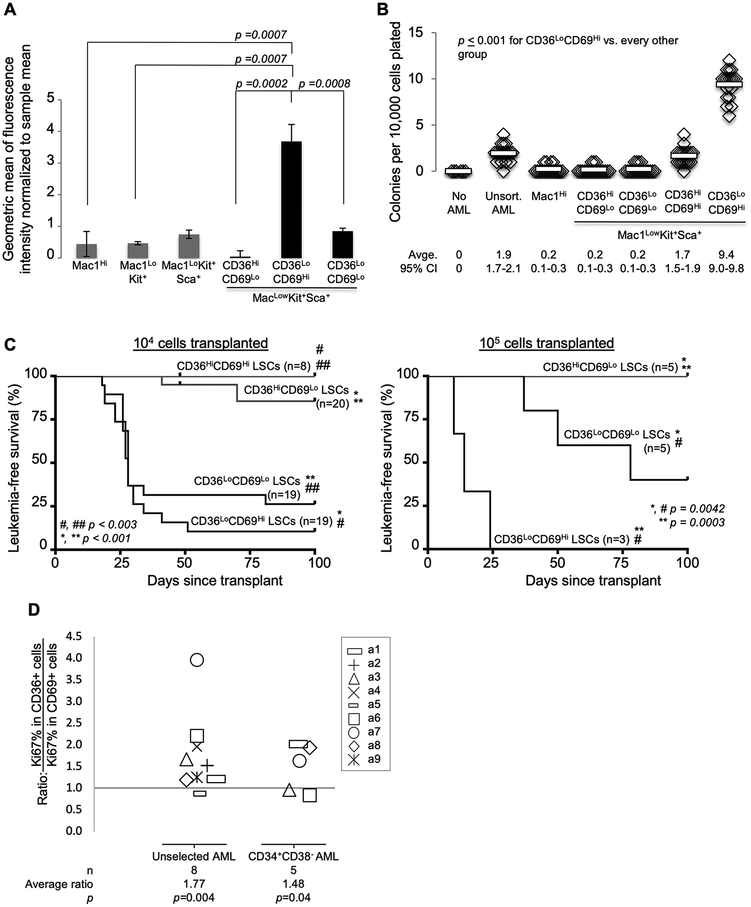
Figure 4.
In vivo leukemia reconstitution assays demonstrate that Group 1 is the self-renewing subset of immunophenotypic LSCs. A, Primary leukemia cells were stained with CellTrace and transplanted into mice via tail vein injection. Leukemia cells were harvested 14 days later. Levels of CellTrace are shown according to immunophenotypic subgroups as assayed by flow cytometry. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. Unpaired Student’s t-test was used to calculate p-values for each comparison indicated. B-C, The LSC-enriched compartment (Mac1LowKit+Sca1+) was sorted based on CD36 and CD69 status. B, Sorted cells were plated in methylcellulose colony forming assays. Results are representative of 4 independent experiments. Horizontal bars indicate mean value. Unpaired Student’s t-test was calculated for each comparison indicated. CI=confidence interval. C, Sorted cells were transplanted into mice via tail vein injection. Each mouse received either 104 or 105 sorted cells (as indicated). Leukemia status was assessed by weekly peripheral blood complete blood counts. MKSCD36HighCD69High were very rare and were therefore not tested at the higher cell dose. Leukemia-free survival is plotted as Kaplan-Meier curves. Log-rank tests were used to calculate p-values. D, The levels of Ki67 (a proliferation marker) were compared between CD36High and CD69High subpopulations of AML. Diagnostic bone marrow aspirates from patients with AML were stained with antibodies to CD34, CD38, CD36, CD69, and Ki67. The ratio of the percentage of cells that express Ki67 in CD36HighCD69Low cells was compared to that of CD36LowCD69High cells within the bulk sample and within the CD34+CD38- (LSC-enriched) compartment. Each symbol represents this ratio in a single sample. Not all samples had sufficient CD36HighCD69Low or CD36LowCD69High cells within the CD34+CD38- compartment for these measurements.