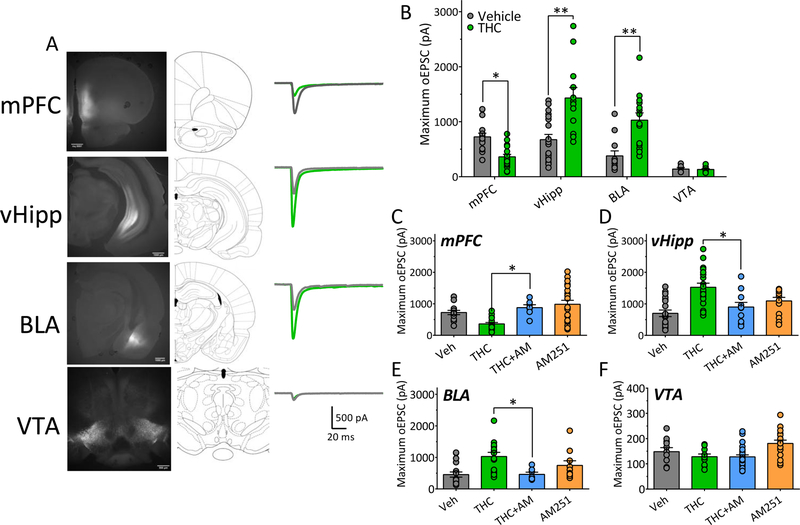
Figure 1. Pathway-specific alteration of NAcs excitatory afferent pathways by chronic Δ9-THC.
A. Representative fluorescence images and corresponding rat brain diagrams of coronal brain slices showing injection sites of ChR2 viruses in brain regions projecting to the NAcs (mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; vHipp, ventral hippocampus; BLA, basolateral amygdala; VTA, ventral tegmental area). At right are representative averages of maximum excitatory postsynaptic current traces (oEPSCs) recorded in NAcs neurons and evoked by 473nm light-activation of ChR2, expressed by afferent axon terminals originating in the brain areas at left. Gray waveforms were obtained from rats treated with vehicle, whereas green traces are those obtained from animals chronically treated with Δ9-THC. B. Mean maximum oEPSCs in NAcs neurons that were evoked by light-stimulation of ChR2 expressed in axons originating in each of the brain regions injected with ChR2-AAV. oEPSCs recorded from both chronic vehicle- and Δ9-THC-injected rats are shown (Two-way ANOVA interaction, F3,100 = 16.2, p <0.0001; Bonferroni post-hoc comparisons, * = p < 0.01, ** = p < 0.0001). C. Maximal light-evoked oEPSCs recorded in the NAcs of rats injected with ChR2 virus in the mPFC after chronic vehicle, Δ9-THC, Δ9-THC preceded by injection of the CB1 antagonist AM251, or AM251 alone (One-way ANOVA, F3,59 = 8.4, p < 0.0001; Holm-Sidak post-hoc comparison of THC vs. THC+AM251, * = p = 0.026). D. Maximal vHipp-evoked oEPSCs recorded after chronic vehicle, Δ9-THC, Δ9-THC preceded by injection of the CB1 antagonist AM251, or AM251 alone (One-way ANOVA, F3,60 = 9.8, p < 0.0001; Holm-Sidak post-hoc comparisons of THC vs. THC+AM251, p = 0.006). E. Maximal BLA-evoked oEPSCs recorded after chronic vehicle, Δ9-THC, Δ9-THC preceded by injection of the CB1 antagonist AM251, or AM251 alone (One-way ANOVA, F3,45 = 6.1, p < 0.01; Holm-Sidak post-hoc comparison of THC vs. THC+AM251, * = p = 0.021). F. Maximal VTA-evoked oEPSCs recorded after chronic vehicle, Δ9-THC, Δ9-THC preceded by injection of the CB1 antagonist AM251, or AM251 alone (One-way ANOVA, F3,62 = 1.02, p = 0.37). Data in C-F illustrate that the effect of chronic Δ9-THC was significantly prevented in mPFC, vHipp, and BLA projections to the NAcs when each injection was preceded by an injection of AM251. Numbers of neurons recorded from number of rats (n/R) in each experiment = A. mPFC, Veh: 16/11, THC: 18/7; vHipp, Veh: 19/8, THC: 12/7; BLA, Veh: 12, THC: 14; VTA, Veh: 6, THC: 11. B. mPFC, Veh: 16/11, THC: 18/7; vHipp, Veh: 19/8, THC: 12/7; BLA, Veh: 12, THC: 14; VTA, Veh: 6, THC: 11. C. mPFC, Veh: 16/11, THC: 18/7, THC+AM: 7/5, AM251: 21/6. D. vHipp, Veh: 19/8, THC: 20/7, THC+AM: 11/4, AM251: 14/5. E. BLA, Veh: 18/7, THC: 14/6, THC+AM: 7/4, AM251: 10/5. F. VTA: Veh: 11/6, THC: 10/6, THC+AM: 32/8, AM251: 17/7.