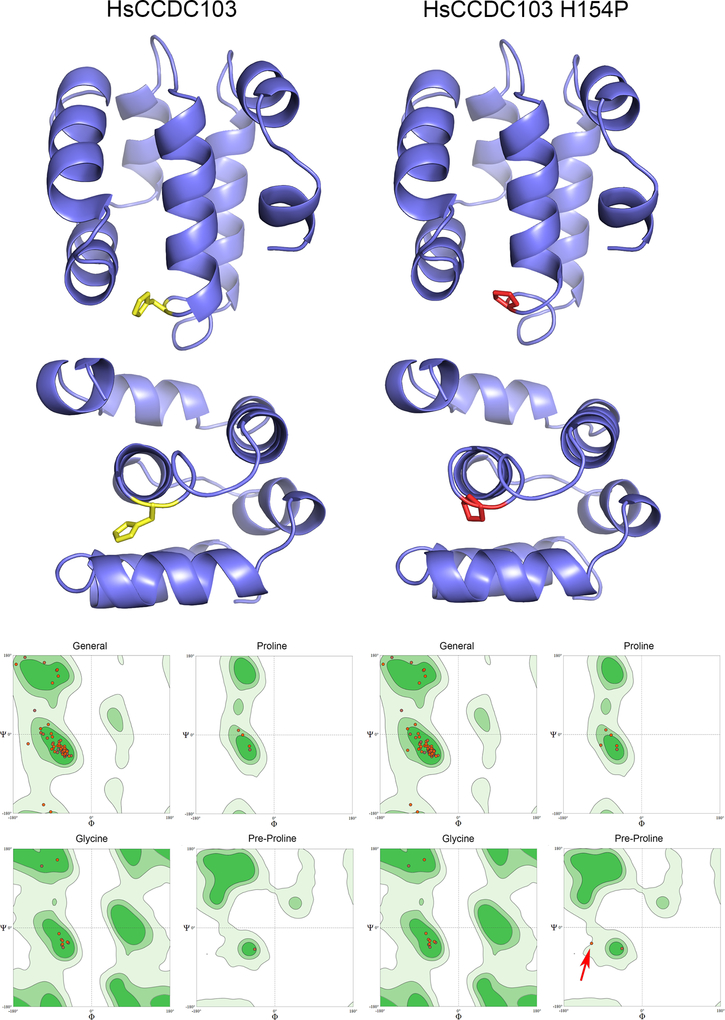
Fig. 5. Molecular Models of the RPAP3_C Domains from Wildtype and H154P Mutant HsCCDC103.
Molecular models for the RPAP3_C domains of wildtype and H154P mutant HsCCDC103 were calculated using SWISSMODEL based on the NMR solution structure of this domain from RPAP3 (PDB 6EZ4). The domain consists of six tightly packed helices. Residue H154 is shown in yellow and when mutated to Pro in red. Ramachandran space plots correlating the Φ and Ψ angles in the peptide backbone for general residues, prolines, glycines and residues preceding proline (when not Gly) are shown for both models; light green indicates sterically allowable regions of the plots; dark green areas are favored regions. In the H154P model, with the exception of the connection between the Pro introduced by the H154P mutation and its preceding residue (red arrow), all Φ/Ψ angles are in allowed and/or favorable regions.