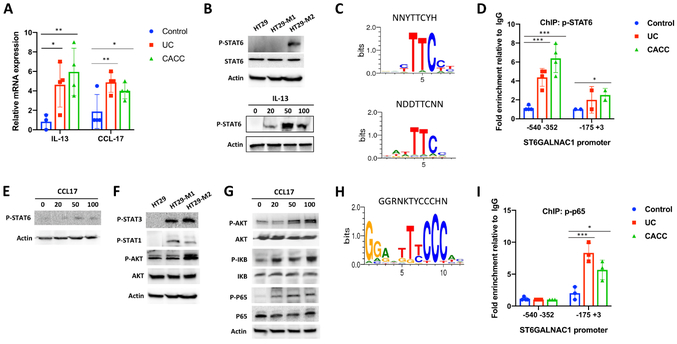
Figure 5. IL-13 and CCL17 induced the transcription activity of ST6GALNAC1 in colon cells of UC and CACC samples.
A and E) The mRNA expression of IL-13 (A) and CCL17 (E) from colon tissues of UC (n=4) and CACC patients (n=4) was detected via qPCR. Non-inflamed colon tissues were used as control (n=4). P values were calculated using a two-tailed t-test. **p<0.01. B) Western blotting analysis of STAT6 and p-STAT6 in HT-29 cells alone or co-cultured with M1 and M2 macrophages (upper panel) or in IL-13-treated HT-29 cells (lower panel). Actin was used as loading control. C and H) The human ST6GALNAC1 promoter region contains putative STAT6-binding sites (C) and p-p65 consensus site (H) detected by MotifMap. D and I) ChIP assays were performed with anti-p-STAT6 (D) and p-p65 (I) Abs followed by Real-Time PCR to measure ST6GALNAC1 promoter in UC, CACC and non-inflamed colon tissues (Control). F and G) Western blotting analysis of indicated proteins in HT-29 cells alone or in CCL17-treated HT-29 cells. P values are calculated using one-way Anova. Error bars represent the SEM (A, D and I) ***p<0.001. All results are representative of three independent experiments.