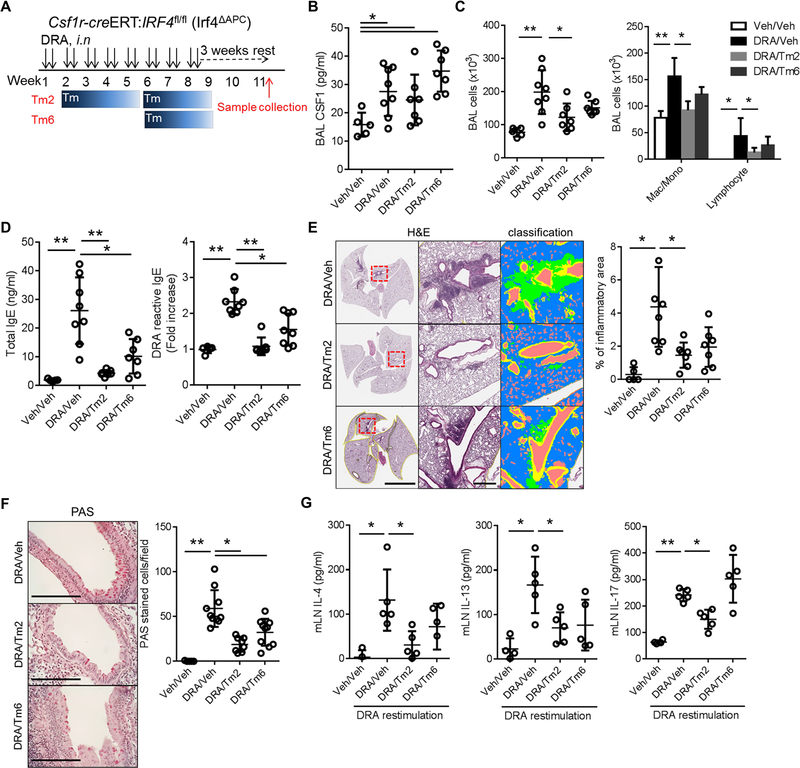
Figure 4. IRF4+ CSF1R+ cells are required for allergen sensitization and Th2 memory in the secondary LNs.
(A) Experimental scheme for depleting CSF1R+IRF4+ antigen presenting cells in Csf1r-creERT;Irf4fl/fl (Irf4ΔAPC) mice. Tm2 and Tm6 indicate that the Tm administration was started at weeks 2 and 6 of the chronic DRA model as depicted. (n=5–8 mice per group) (B) Depletion of CSF1R+IRF4+ in Irf4ΔAPC mice had no effect on BAL CSF1 concentration. (C-F) However, depletion of CSF1R+IRF4+ from week 2 (Tm2) resulted in a modest decrease in BAL inflammatory cells, significant reduction of total and DRA-reactive serum IgE, marked reduction of chronic lung inflammation and goblet cell metaplasia. The Tm6 group showed similar trends, but was less effective than in the Tm2 group. Left and middle scale bars in (E) are 5 mm and 500 μm, respectively. (G) Single cell suspensions of LNs were isolated from each group and re-stimulated with DRA for 72 hours. The cytokines in culture supernatants were measured. The re-stimulation with DRA boosted the secretion of IL-4, IL-13 and IL-17, compared to the sham-treated control. However, the Tm treated groups showed a blunted response for IL-4 and IL-13 production, whereas IL-17 secretion in the Tm 6 group was not affected by Tm treatment while the Tm2 group showed a mild decrease in IL-17 production. * p<0.05, **p<0.01