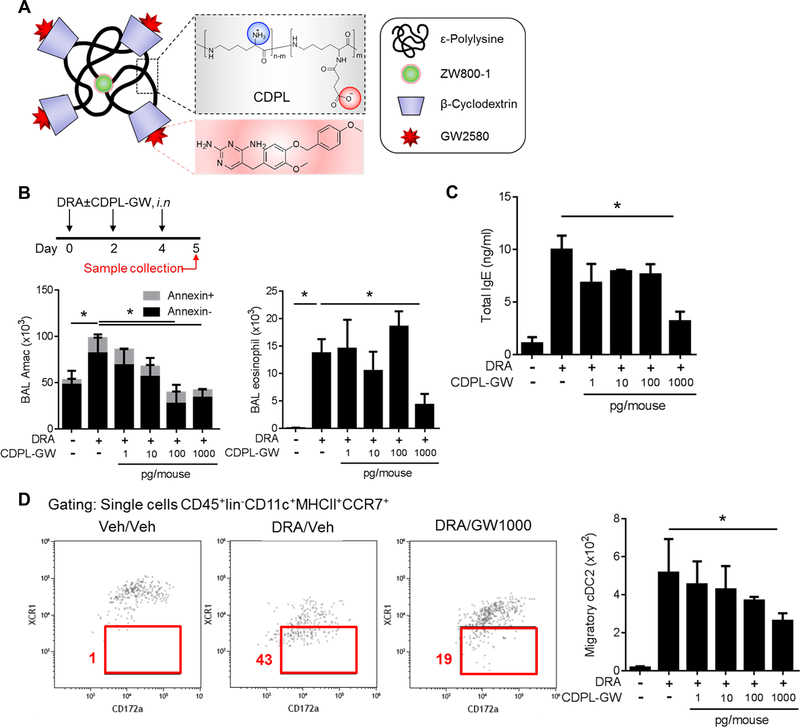
Figure 5. CDPL-GW nanoprobe carrying CSF1R inhibitor block cDC2 migration and allergen sensitization.
(A) Structure of the CDPL-GW nanoprobe which carries 4 molecules of GW2580, a selective CSF1R inhibitor and a ZW800–1 fluorescent dye. (B-C) The experimental scheme to optimize the dose of CDPL-GW. The total AM count and annexin V+ AMs in BAL fluids were measured by flow cytometry. AMs and eosinophils in BAL fluids were identified by CD11c+SiglecF+, CD11c−SiglecF+ respectively. DRA challenge induced increases in BAL AMs and eosinophils, which was inhibited by the CDPL-GW treatment in a dose dependent manner. However, there was no change in the proportion of annexin V+ cells up to 1ng (=1000pg) of CDPL-GW /mouse which was a sufficient dose to suppress the BAL eosinophil recruitment and total serum IgE rise (n=4–5 mice per group). (D) Migratory DCs (defined by CD45+lineage−CD11c+MHCll+CCR7+) were measured in the single cell suspensions isolated from mediastinal LNs. The number of migratory DCs in LNs gradually declined as the dose of CDPL-GW inhibitor was increased via the intranasal route (n=4–5). * p<0.05