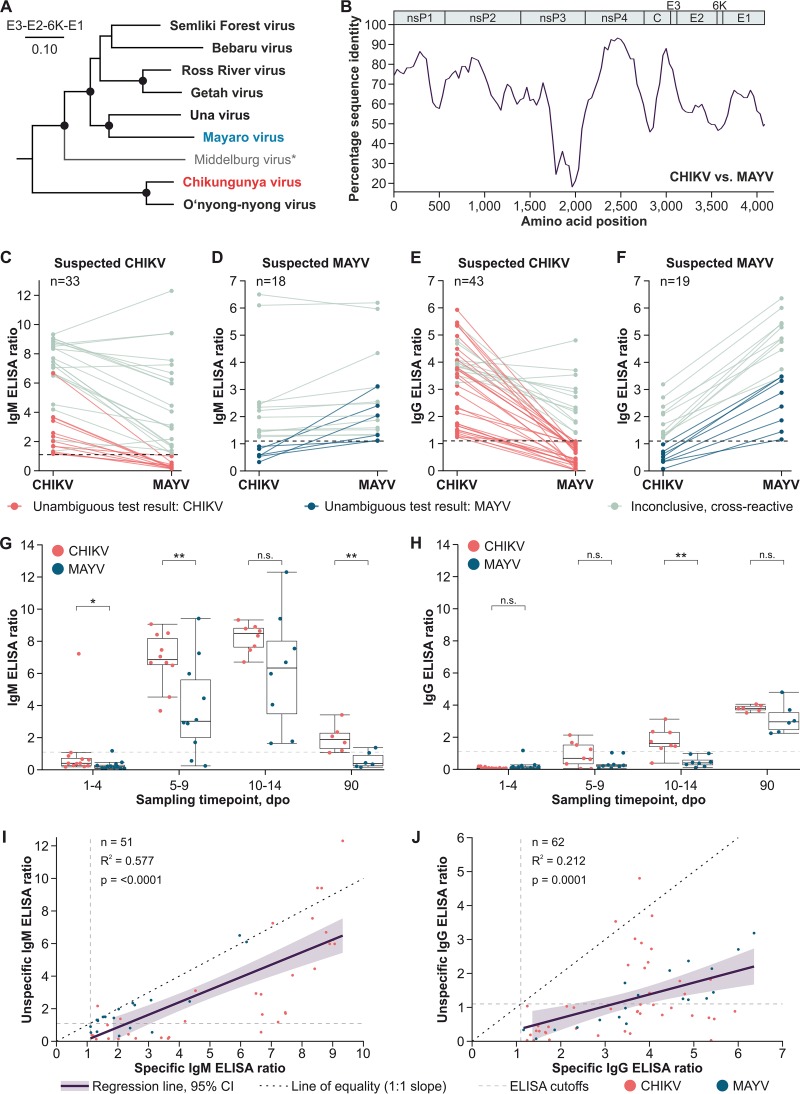
FIG 1.
Phylogeny, antibody kinetics, and ELISA cross-reactivities of CHIKV and MAYV. (A) Maximum likelihood phylogeny of members of the Semliki Forest serocomplex based on translated amino acid sequences of the envelope and 6K protein-coding domains. A Whelan and Goldman substitution model was used in MEGA-X (https://www.megasoftware.net), with a discrete gamma distribution of site-specific rates and a complete deletion option. Statistical support of grouping was determined by 500 bootstrap replicates. For all viruses, the ICTV reference sequences were used (https://talk.ictvonline.org/ictv-reports/ictv_online_report/positive-sense-rna-viruses/w/togaviridae/872/genus-alphavirus). *, Middelburg virus was included to show the complete phylogeny, although it likely forms a distinct serocomplex. (B) Percentage amino acid sequence identity between CHIKV and MAYV calculated using the ICTV reference sequences and SSE version 1.3 (http://www.virus-evolution.org/Downloads/Software/), with a fragment length of 400 and an increment between fragments of 100 amino acid residues. (C) CHIKV and MAYV IgM ELISA reactivities in Brazilian CHIKV-specific sera. (D) CHIKV and MAYV IgM ELISA reactivities in Peruvian MAYV-specific sera. (E) CHIKV and MAYV IgG ELISA reactivities in Brazilian CHIKV-specific sera. (F) CHIKV and MAYV IgG ELISA reactivities in Peruvian MAYV-specific sera. (G) Median CHIKV and MAYV IgM ELISA reactivities of longitudinally sampled CHIKV-specific sera. *, P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; n.s., differences were not significant. (H) Median CHIKV and MAYV IgG ELISA reactivities of longitudinal CHIKV-specific sera over time. (I) Linear regression of specific and unspecific CHIKV and MAYV IgM ELISA reactivities. 95% CI, 95% confidence interval. (J) Linear regression of specific and unspecific CHIKV and MAYV IgG ELISA reactivities. All nonlongitudinal samples were classified based on serologic test results. Conducted ELISAs are based on comparable recombinant structural proteins and CE (Conformité Européenne) labeled. For each ELISA, 1 μl patient serum was diluted 1:101 with sample buffer and applied to antigen-covered test wells. Human antibodies bound to the antigens were next targeted by peroxidase-labeled anti-human secondary antibodies. Afterwards, a substrate solution was added. The substrate was oxidized if peroxidase-labeled anti-human secondary antibodies were present, increasing the absorbance of the substrate solution. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm wavelength. Ratios were calculated using a calibrator sample provided in the kits.