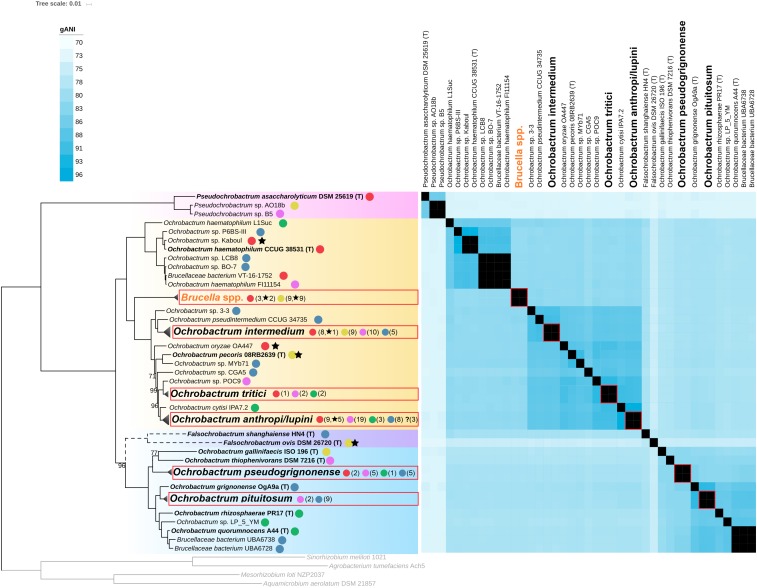
FIGURE 2.
ML Phylogenetic tree of the Brucellaceae clade. The tree was computed using RaxML from an alignment of 195 core proteins, and rooted using four members of the Rhizobiaceae and Phyllobacteriaceae families (depicted in gray). Branching support was estimated using 100 bootstrap replicates, with only values lower than 100% displayed. Genomes of type strains are in bold font. The Pseudochrobactrum clade is indicated with pink background, the Falsochrobactrum in purple background, and the Ochrobactrum Clades 1 and 2 are indicated with orange and blue backgrounds, respectively. Monophyletic clades corresponding to genomic species and including 5 genomes or more are collapsed and boxed in red. Branching of Falsochrobactrum spp. is depicted in dashed lines to reflect conflicting topology with the phylogeny displayed in Figure 1. Origin of strain isolation is indicated with a colored dot: red, human; yellow, animal; pink, anthropized environment; green, plant rhizosphere; blue, other (environmental). Numbers in parenthesis indicate the number of genomes of each origin for collapsed clades. Stars indicate human or animal clinical isolates. The heatmap represent pairwise genome gANI values from 70 (light blue) to 96.5 (deep blue). Values larger than 96.5 (the genomic species threshold) are displayed in black. Collapsed gANI values are boxed in red.