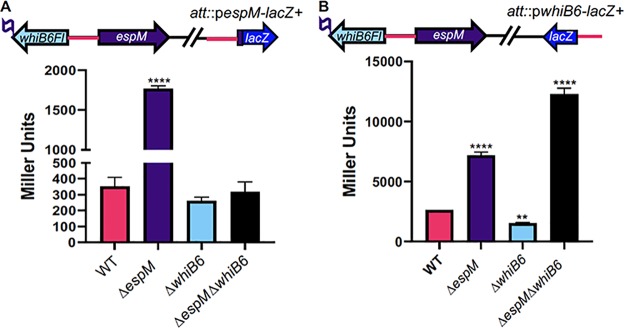
FIG 4.
EspM and WhiB6 mutually regulate the expression of the espM and whiB6 genes. (A) The whiB6/espM locus and the espM-lacZ+ transcriptional fusion integrated at the attB site in M. marinum. The flag at the C terminus of the whiB6 gene indicates the presence of the whiB6Fl allele. Data represent β-galactosidase activity of the espM-lacZ+ transcriptional fusion. Error bars represent propagated errors. A one-way ordinary ANOVA (P < 0.0001) followed by a Sidak’s multiple-comparison test was performed. Significance is shown relative to the WT strain. ****, P < 0.0001. (B) The whiB6/espM locus and the whiB6-lacZ+ transcriptional fusion integrated at the attB site in M. marinum. Data represent β-galactosidase activity of the whiB6-lacZ+ transcriptional fusion. Error bars represent propagated errors. A one-way ordinary ANOVA (P < 0.0001) followed by a Tukey’s multiple-comparison test was performed. Significance data shown are relative to the WT strain. ****, P < 0.0001; **, P = 0.0078. For both panels, the data represent averages of results from at least three biological replicates, each performed in technical triplicate. All strains indicated in Fig. 4, with the exception of the ΔwhiB6 and ΔwhiB6 ΔespM strains, contained a C-terminal epitope tag on the whiB6 gene.