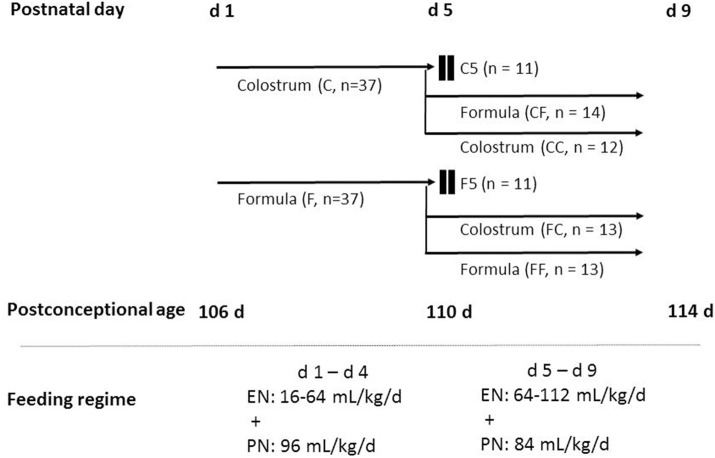
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the animal experimental design. Seventy-four preterm pigs from four sows were delivered at 106 days gestation. The pigs were stratified according to birth weight and gender and allocated randomly into two groups: one group receiving colostrum (C, n = 37) and the other group receiving formula (F, n = 37) for 4 days until day 5 of the experiment. On day 4, pigs in each group were further stratified into three groups to be euthanized on day 5, fed the same feeding for another 4 days, and fed the other diet for another 4 days resulting in six groups: colostrum feeding until day 5 (C5, n = 11), formula feeding until day 5 (F5, n = 11), colostrum feeding for 4 days followed by formula until day 9 (CF, n = 14), colostrum feeding until day 9 (CC, n = 12), formula feeding for 4 days followed by colostrum until day 9 (FC, n = 13), and formula feeding until day 9 (FF, n = 13). Pigs received gradually increasing volumes of enteral nutrition 16–64 ml kg−1 day−1 on days 1–4 and 64–112 ml kg−1 day−1 on days 5–8. Parenteral nutrition was given at decreasing rates of 96–84 ml kg−1 day−1. C, colostrum; EN, enteral nutrition; F, formula; PN, parenteral nutrition.