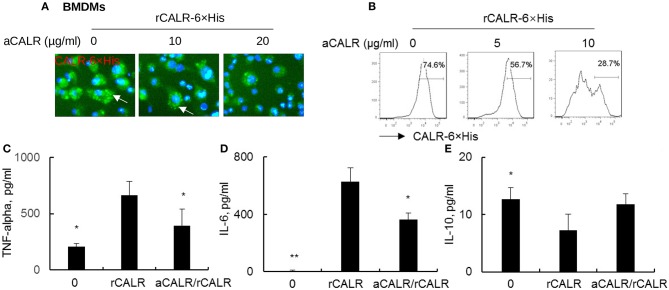
Figure 2.
anti-CALR antibody (aCALR) inhibited recombinant CALR (rCALR) binding to macrophages and suppressed the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were treated with 2 μg/ml rCALR-6×His with or without pre-neutralization with 5, 10, and 20 μg/ml aCALR. (A) Twenty-four hours after the treatment, rCALR-6×His binding to BMDMs was analyzed by incubation with FITC-conjugated anti-His antibody. White arrow indicates the punctuated positive stanning on cell surface. One representative photograph of three independent experiments. (B) rCALR-6×His positive cells were quantitatively analyzed by flow cytometry analysis. The expression level of TNF-alpha (C), IL-6 (D), and IL-10 (E) in the cell supernatants was analyzed by ELISA analysis. In the aCALR/rCALR group, rCALR was neutralized with 5 μg/ml aCALR (C,D) or 10 μg/ml aCALR (E), respectively. Data was presented as mean ± standard error, n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. rCALR-treated cells.