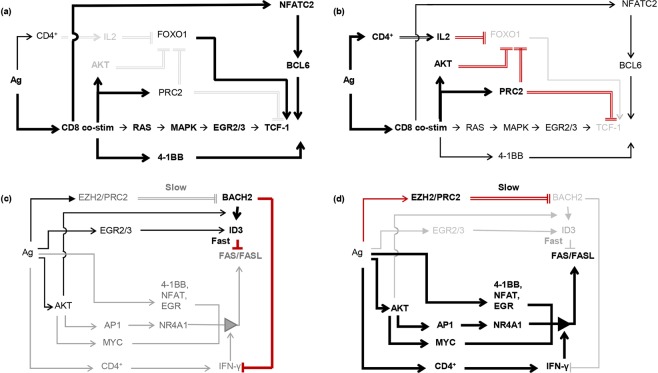
Figure 4.
Two-state models of the incoherent feed-forward loops (iFFLs) regulating TCF-1 and FAS/FASL activity. (a) The early state of the TCF-1 iFFL. Thick black lines indicate active regulatory interactions. Light gray lines and text indicate inactive interactions and genes. TCF-1 and FOXO1 are expressed in naïve CD8+ T cells. TCF-1 expression during early CD8+ T cell activation is maintained via direct regulation by FOXO1, and via MAPK signaling activation of ERG2/3, via 4-1BB signaling, and through calcium-activated NFATC2. The 2 repressive regulators of TCF-1, EZH2/PRC2 signaling and PI3K/AKT signaling, are inactive at this stage. AKT activation in stimulated CD8+ cells peaks at ~day 5 post-infection63. EZH2/PRC2 activity peaks at around 4 days post-infection30. (b) At around 3 days post-infection, AKT represses FOXO1 activity, while PRC2 initiates a chain of events culminating in DNA-methylation and transcriptional shut-down of FOXO1 and TCF-1 genes. IL2 signaling also becomes active around this time and suppresses FOXO1 activity. Thin black lines indicate activating inputs overridden by dominant inhibitory inputs. (c,d) illustrate the early and late states of the FAS/FASL signaling iFFL using the same notation as in (a,b). In (c), BACH2 and ID3 are active in naïve and early activated CD8+ cells, and block FAS/FASL expression and signaling. At later time points (d), EZH2/PRC2 activity suppresses BACH2/ID3. IFN-γ signaling becomes activated and facilitates activation of FAS/FASL by 4-1BB, NFATs, EGRs, and NR4A1.