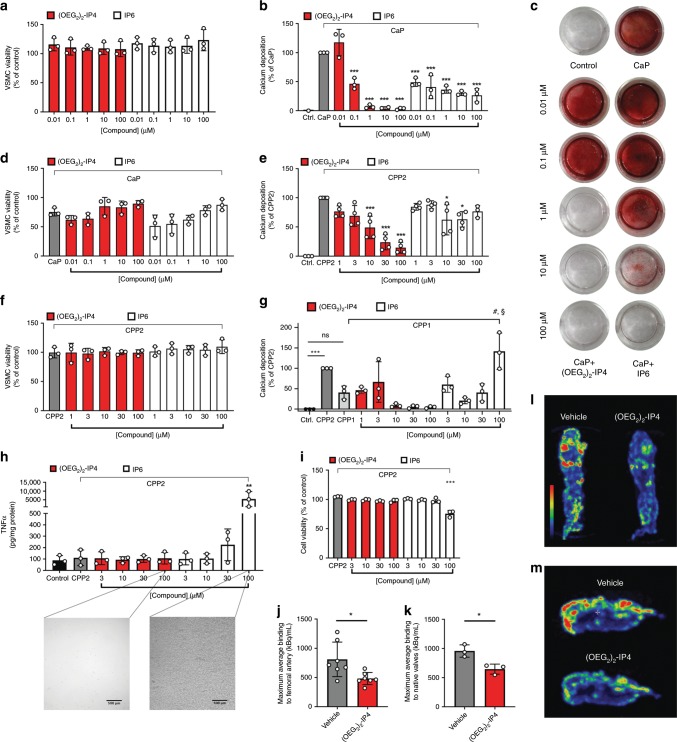
Fig. 3. (OEG2)2-IP4 abrogates in vitro VSMC calcification and 18F-NaF uptake onto calcified human explants.
a, d, f VSMC viability as determined by the MTS assay compared to medium control. b, c VSMC calcification was induced by high-CaP medium and the effect of cell treatment with IP6 or (OEG2)2-IP4 was investigated quantitatively by colorimetric analysis of cellular calcium deposition after 5 days control (calcium deposition in mass units in Ctrl. ranged between 81 and 622 µg Ca/mg protein) (b) and qualitatively by Alizarin Red staining for calcium (c) in a 24-well plate setup compared to medium control. e, g Same as b but calcium deposition was induced by CPP2- (e) and CPP1- (g) supplemented medium (50 µg Ca/mL), respectively (calcium deposition in mass units in Ctrl. ranged between 189 and 734 µg Ca/mg protein in e). h TNFα concentration in human macrophage supernatants after exposing cells to CPP2 (50 µg Ca/mL) and compounds as assessed by immunoassay. High concentrations of IP6, but not (OEG2)2-IP4, precipitated in the treatment medium as shown in the insets and resulted in significantly increased TNFα levels in supernatants (scale bar = 500 µm). i Macrophage viability as determined by the MTS assay compared to medium control. j, k, l, m Incubation of severely calcified human femoral arteries (j, l) or human aortic valves (k, m) with (OEG2)2-IP4 and without (vehicle) resulted in a reduction of 18F-NaF uptake in (OEG2)2-IP4 samples compared with baseline vehicle studies as evident from the maximum average 18F binding determined by 18F-NaF-PET imaging (j, k) and the maximum intensity projections of collected 18F-NaF-PET data (l, m). All data are expressed as mean ± s.d. n = 7 (j) and n = 3 (k) biologically independent samples, and from n = 4 (e) and n = 3 (all others) independent cell experiments. Statistical significance was calculated from an ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test or from an unpaired Student’s t-test to determine significance between two data sets with *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. gray bar, #p < 0.001 vs. CPP1, and §p < 0.001 vs. 100 µM (OEG2)2-IP4.