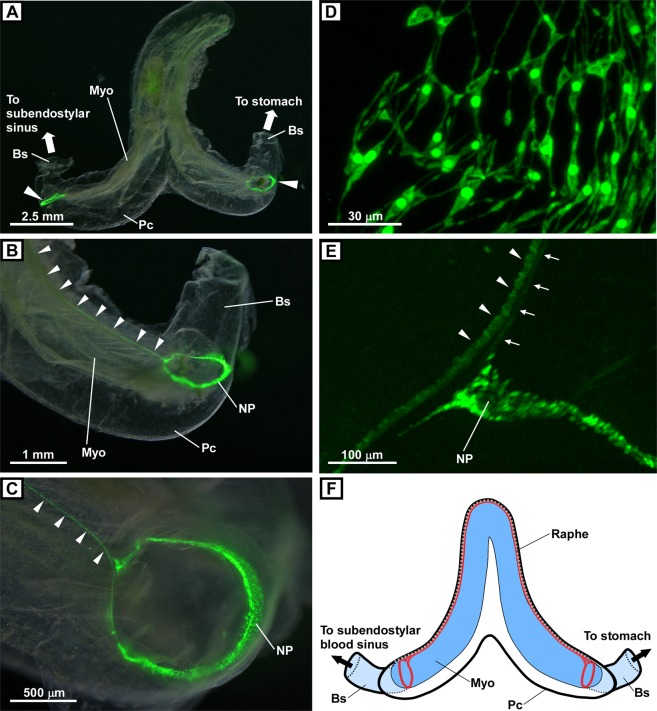
Figure 5.
PC2 promoter-driven Kaede-positive cells in the heart. (A) Overview of the heart. The myocardium surrounded by the pericardium and blood sinuses connecting to both terminals of the heart are shown. Kaede-positive cells forming a ring-shaped structure at both terminals of the heart are shown (arrowheads). (B) Magnified image of the right terminal of the heart. The ring-shaped structure of the Kaede-positive cells in the terminal of the myocardium is shown. Kaede signals along the raphe are also shown (arrowheads). (C) Magnified image of the right terminal of the heart. The ring of the Kaede-positive cells appeared not to be closed, and a major Kaede-positive tract emerged from one end of the ring and runs along the raphe (arrowheads). (D) Magnified image of the Kaede-positive cells in the ring-shaped nerve plexus in the heart. Numerous Kaede-positive neurons forming networks are shown. (E) Magnified image of the Kaede-positive tract emerging from the nerve plexus. Major and minor Kaede-positive tracts are indicated by arrowheads and arrows, respectively. (F) Schematic illustration of the heart. The myocardium is shown in blue. Blood sinuses are shown in light blue. The raphe, which connects the pericardium and myocardium, is indicated by a gray dotted line. The ring of Kaede-positive cells and tracts are indicated by a red line. The images in (A–C) were obtained under a fluorescence stereomicroscope as a superimposed image. The images in (D,E) were obtained under a confocal laser scanning microscope, and the image in (D) was obtained as a z-stack image. Bs, blood sinus; Myo, myocardium; NP, nerve plexus; Pc, pericardium.