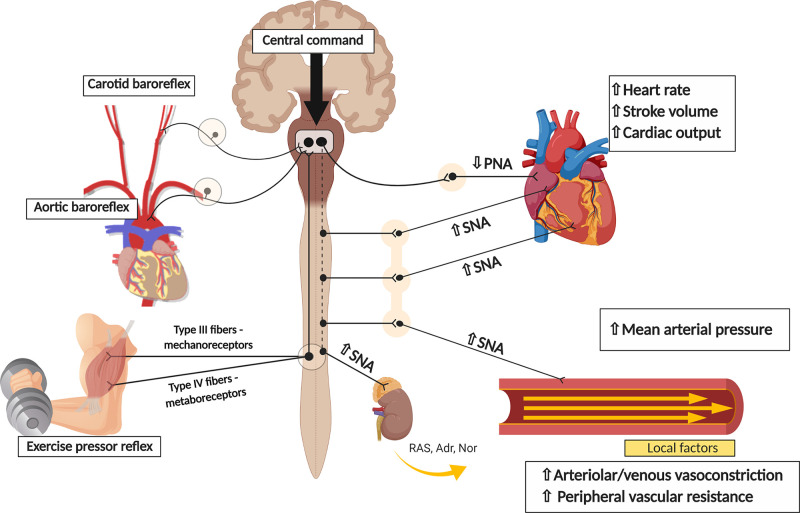
Fig. 1.
Cardiovascular adjustments to exercise: the role of the autonomic nervous system. During exercise, feedforward signals from higher brain areas (i.e., central command) and feedback information arising from different somatic and visceral afferents (i.e., such as the arterial baroreflex and the exercise pressor reflex) convey sensory information to the central nervous system, which then coordinates the efferent response to the cardiovascular system. SNA, sympathetic nerve activity; PNA, parasympathetic nerve activity; RAS, renin–angiotensin system; Adr, adrenaline; Nor, noradrenaline.