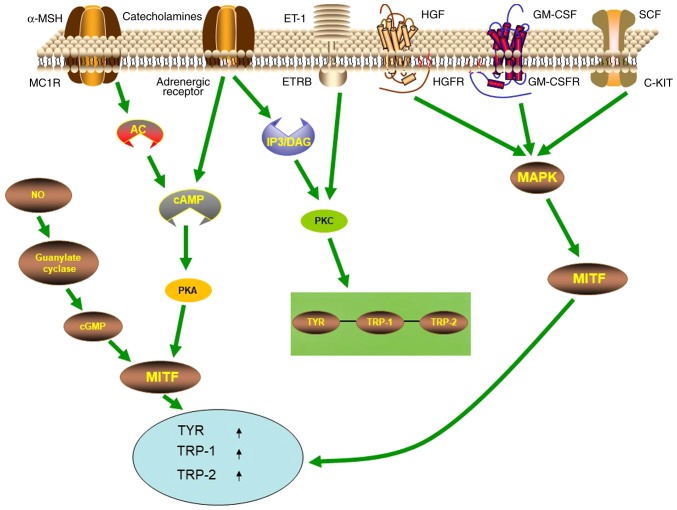
Figure 1.
Different signaling pathways regulating melanogenesis. Upon binding to MCIR and adrenergic receptor respectively, α-MSH and catecholamines activate the PKA pathway by increasing cAMP. Then PKA promotes MITF expression, which controls the expression of melanogenesis-related genes TYR, TRP-1 and TRP-2. Upon binding to ETR and adrenergic receptor respectively, ET-1 and catecholamines activate the PKC pathway to promote the expression of TYR, TRP-1 and TRP-2. Upon binding to c-MET, GM-CSFR, and c-KIT and respectively, HGF, GM-CSF, and SCF activate the MAPK pathway to promote the expression of MITF, which in turn increases the expression of TYR, TRP-1 and TRP-2. In addition, NO in the cytoplasm regulates MITF-driven expression of TYR, TRP-1 and TRP-2 through the guanylate cyclase-cGMP pathway. α-MSH, α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone; MC1R, melanocortin-1 receptor; ET-1, endothelin-1; ETR, ET-receptor; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSFR, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor; SCF, stem cell factor; AC, adenylate cyclase; cAMP, 3′5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; c-GMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; IP3/DAG, inositol trisphosphate/diacylglycerol; PKC, protein kinase C; MAPK, mitogen activated protein kinase; TYR, tyrosinase; TRP-1, tyrosinase-related protein-1; TRP-2, tyrosinase-related protein-2.