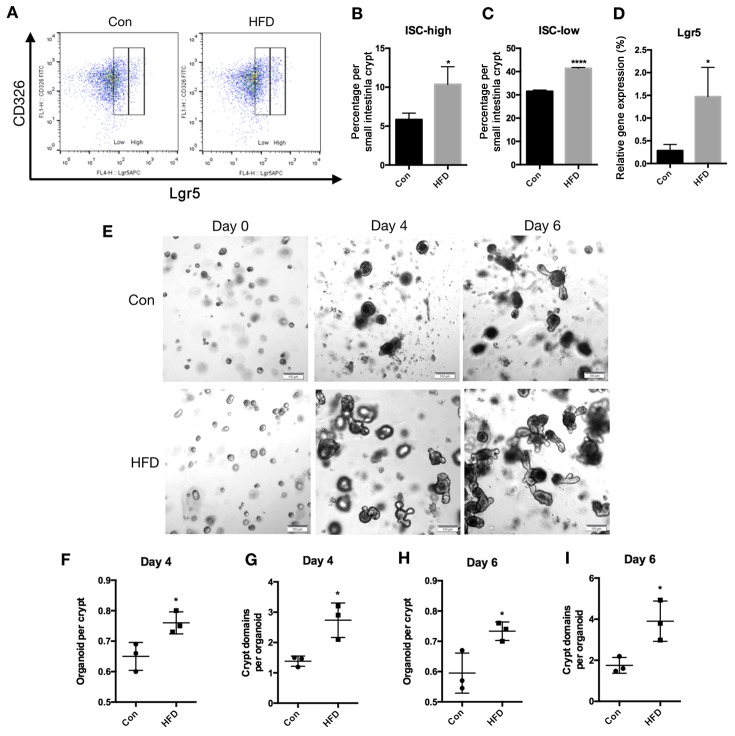
Figure 3.
An HFD increases the ISC count and crypt function in the small intestine of mice. Small intestinal crypts and villi were isolated and epithelial cell suspensions were dissociated into single cells. (A) Representative flow cytometry analysis showing Lgr5 expression in the CD326 cell population obtained from the small intestine. (B) ISCs defined as Lgr5high, and (C) progenitor cells defined as Lgr5low in the entire small intestine. (D) mRNA expression of Lgr5 in the small intestine. (E) Small intestinal crypts were isolated and cultured in Matrigel to develop organoid colonies. Representative images of small intestinal organoids at days 0, 4 and 6 are displayed (scale bar, 100 µm; magnification, ×20). (F) Organoids formed per crypt and (G) crypt-domains per organoid on day 4. (H) Organoids formed per crypt and (I) crypt-domains per organoid on day 6. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05 and ****P<0.0001, vs. Con group. HFD, high-fat diet; ISC, intestinal stem cell; Con, control.