Figure 4.
Polyclonal CD8+ T Cells Show Stronger Homeostatic TCR Signaling Than CD4+ T Cells
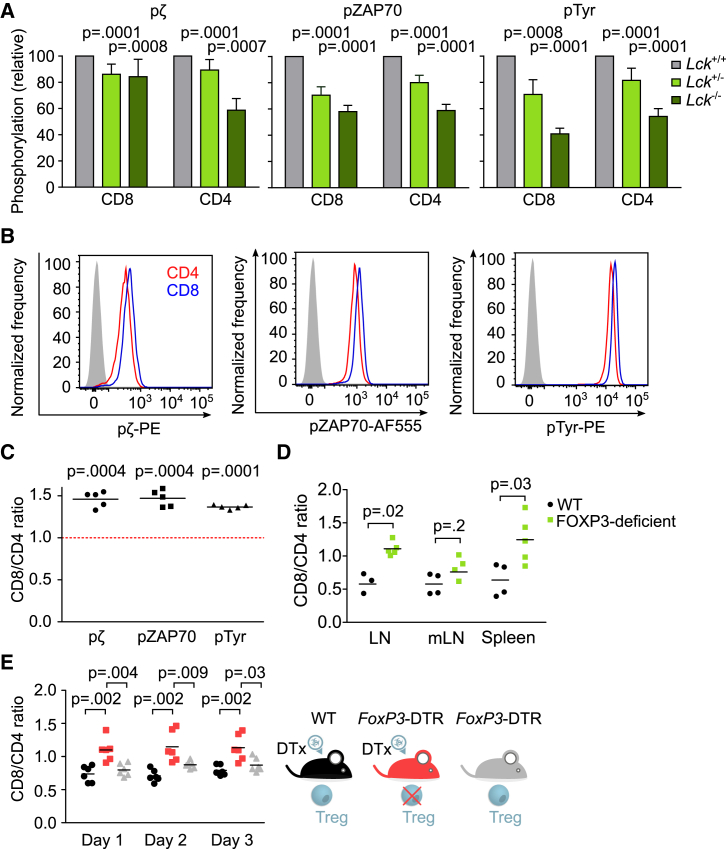
(A–C) Fixed and permeabilized LN T cells from WT mice were stained with antibodies to TCRβ, CD4, CD8, pTCRζ chain, pZAP70, and overall tyrosine phosphorylation and analyzed by flow cytometry. Comparison of basal signaling in CD8+ CD44− and CD4+ CD44− T cells from Lck+/+, Lck+/−, and Lck−/− mice. Phosphorylation level (geometric mean fluorescence intensity [gMFI]) relative to Lck+/+ mice is shown. Mean + SEM; n = 7 mice in 7 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by one sample t test (hypothetical mean value = 1) (A). Comparison of basal signaling in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. A representative experiment out of 5 independent experiments in total (B). Ratio of phosphorylation levels (gMFI) of CD8+ versus CD4+ peripheral T cells in pTCRζ, pZAP70, and overall tyrosine phosphorylation for each mouse. Mean; n = 5 mice in 4 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by one sample t test (hypothetical mean value = 1) (C).
(D) The LN, mLN, and splenic T cells of Foxp3-deficient mice and their WT littermates were analyzed by flow cytometry. The ratio of CD8+ to CD4+ T cells is shown. Mean; n = 4–5 mice from 2 experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by 2-tailed Mann-Whitney test.
(E) The peripheral LN T cells from Foxp3-DTR mice after the administration of diptheria toxin, untreated Foxp3-DTR mice, and WT mice after the administration of diptheria toxin were analyzed. The ratio of CD8+ to CD4+ T cells is shown. n = 6 mice in 3 independent experiments; mean. Statistical analysis was performed by 2-tailed Mann-Whitney test.
See also Figure S4.