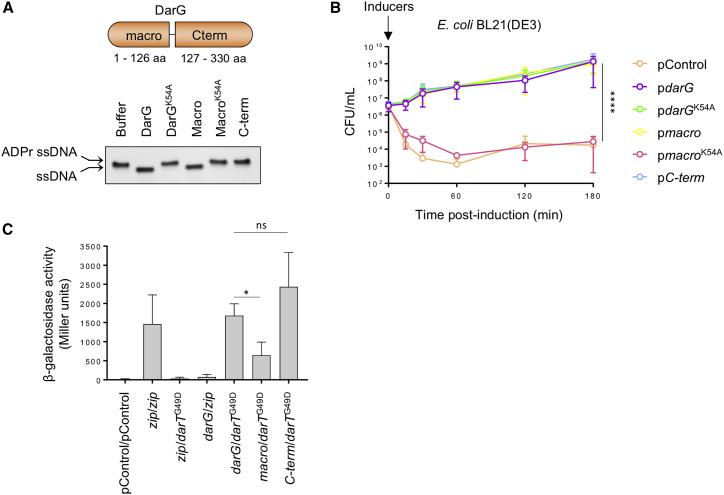
Figure 2.
DarG Counteracts DarTG49D Toxicity
(A) De-ADP-ribosylation of a 27-mer ADP-ribosylated ssDNA oligonucleotide incubated with purified EPEC DarG, DarGK54A, the macrodomain (Macro) of DarG, MacrodomainK54A (MacroK54A), or the C-terminal domain (C-term) of DarG. ADPr ssDNA, ADP-ribosylated ssDNA; n = 3, data from one experiment shown.
(B) Viability of E. coli BL21(DE3) following expression of darTG49D with different versions of darG. pControl, empty plasmid; n = 3 ± SD, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA.
(C) Bacterial two-hybrid assay of E. coli BTH101 containing pUT18 expressing T18 fused to zip, darG, macro, or C-term and pKT25 expressing T25 fused to zip or darTG49D. pControl, empty pUT18 or pKT25; Zip, Zipper leucine, used as a positive control; ns, not significant; n = 3 ± SD, ∗p < 0.05 by Student’s t test.