Figure 7.
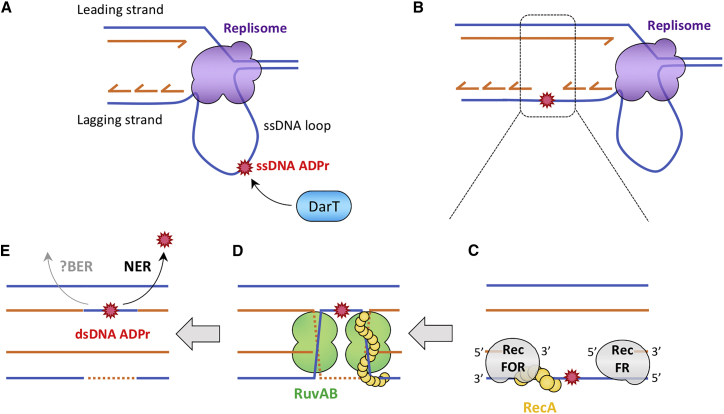
Model: EPEC DarT ADP-Ribosylates ssDNA and Stalls DNA Replication
(A) DNA replication generates ssDNA loops, potential substrates for DarT.
(B) Toxicity due to the presence of ADPr on ssDNA loops is unaffected by translesion polymerases and might lead to the generation of SSGs after DNA replication.
(C) RecFOR binds both extremities of the SSG and facilitates RecA nucleoprotein formation on ssDNA. RecA polymerization induces the SOS response and catalyzes the strand migration of the ssDNA into the homologous dsDNA, resulting in the formation of two Holliday junctions that are stabilized by RuvAB.
(D) Junctions are then resolved by RuvC or RecG, generating two dsDNA molecules, with one of them containing dsDNA ADPr.
(E) NER pathway is recruited in a RecF-dependent manner to deal with the dsDNA ADPr, although BER might also contribute.