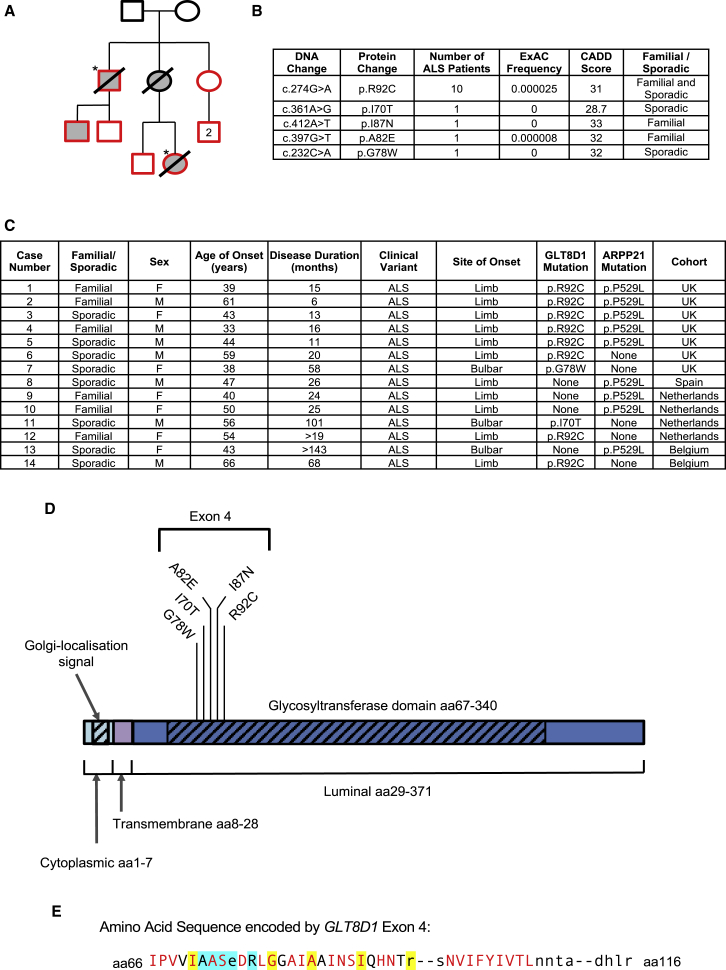
Figure 1.
Discovery of ALS-Associated Mutations within Exon 4 of GLT8D1 in Close Proximity to the Putative Substrate Binding Site
(A) Original pedigree in which p.R92C mutations were discovered. Exome sequencing was performed in two related individuals with ALS (∗). Sanger sequencing (of red shapes) confirmed the p.R92C mutation is carried by ALS patients (shaded gray) and absent from unaffected individuals.
(B) Rare deleterious mutations identified within exon 4 of GLT8D1.
(C) Phenotype information for patients carrying mutations in GLT8D1 and/or ARPP21.
(D) Identified structural and topological domains within GLT8D1, including the site of identified mutations within exon 4.
(E) Sequence homology analysis within exon 4 localizes ALS-associated mutations to close proximity with the substrate binding site of GLT8D1. ALS-associated amino acid changes (yellow highlight) affect evolutionary conserved bases (red text) with one exception. Amino acids which form the putative substrate binding site are indicated (blue highlight). Displayed sequence is glycosyltransferase domain encoded by exon 4 (amino acid [aa] 66–aa116).