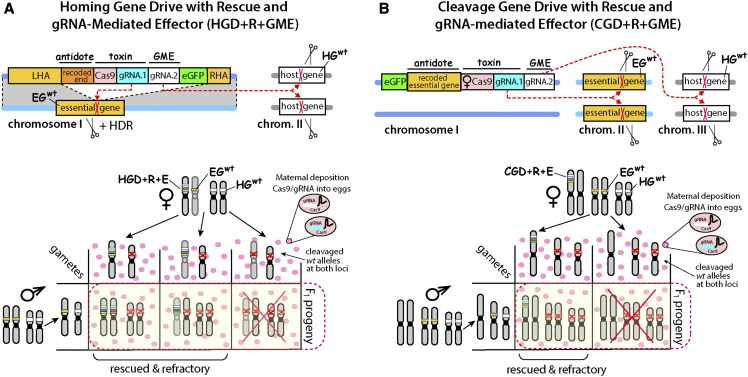
Figure 4.
gRNA-mediated effector (GME) incorporated into two novel gene drive designs mechanistically based on lethal biallelic mosaicism. (A) Schematic of Homing Gene Drive targeting an essential gene with a recoded Rescue and GME (HGD+R+GME). The HGD+R+GME expresses Cas9 and two gRNAs targeting an essential gene (EG) and host gene (HG), a marker gene (eGFP), and the cleavage-resistant recorded portion of the essential gene that is being targeted by the gRNA/Cas9 complex (Rescue), which can rescue the knockout phenotype, flanked by Left and Right Homology Arms (LHA and RHA). Mechanistically, once HGD+R+GME is integrated precisely inside the EG it will direct cleavage of the EGwt allele on a receiver chromosome, and induce knockout mutations that will either result in lethal biallelic mosaicism, or convert the receiver chromosome into EGHGD+R+GME via homology directed repair (HDR). This ensures that only the progeny that inherit EGHGD+R+GME survive, while all progeny that inherit a cleaved EG allele perish due to non-rescued lethal mosaicism. In addition, the HGD+R+GME induces knockout of HG located on another (or the same) chromosome, leading to desired phenotype (i.e., pathogen resistance) to its carriers. The Punnett square below depicts the genetics of how HGD+R+GME achieves a 100% transmission rate and refractoriness in F1 progeny. Female heterozygous for HGD+R+GME maternally deposits Cas9/gRNA complexes into every oocyte knocking out both EG and HG, and only zygotes that inherit the HDR+R+GME would survive as F1 progeny. Notably, HDR will convert EGwt alleles into EGHGD+R+GME alleles and further increase numbers of surviving F1 progeny and this non-Mendelian inheritance rate will depend on homing efficiencies. (B) Schematic of Cleavage-only Gene Drive targeting an essential gene with a recoded Rescue and GME (CGD+R+GME). The CGD+R+GME expresses Cas9 with multiple gRNAs targeting an ES (gRNA.1) and HG (gRNA.2), a marker gene (eGFP), and the cleavage-resistant recorded essential gene (Rescue) integrated at a separate genomic location from the target gene. Mechanistically, a CGD+R+GME drive relies exclusively on cleavage with no HDR required for biased inheritance. A Punnett square depicts the genetics of how CGD+R+GME achieves 100% transmission and infection resistance rates in F1 progeny. The female heterozygous for CGD+R+GME deposits Cas9/gRNA complexes into every oocyte, only the half of the zygotes that inherits the CDR+R+MGE in a Mendelian fashion survive as F1 progeny, while the other half that do not inherit CDR+R+GME perishes due to lethal biallelic mosaicism.