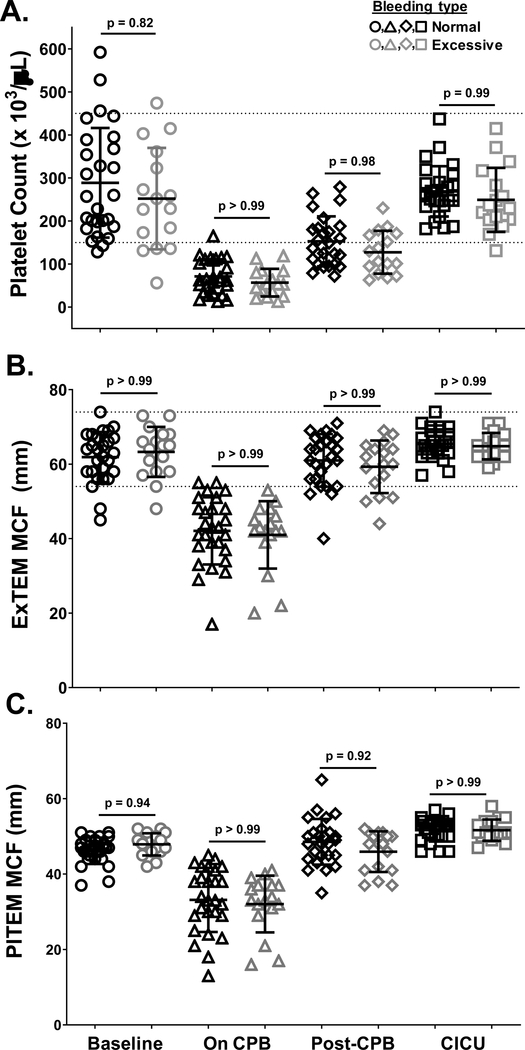
Figure 6. Platelet counts and platelet-dependent Rotational Thromboelastometry (ROTEM) values changed similarly over the course of CPB surgery in neonates who bled excessively following surgery relative to those who did not.
WB samples were drawn from patients prior to initiation of CPB surgery (Baseline, circles), after completion of surgery but before separation from CPB (On CPB, triangles), after separation from CPB and prophylactic transfusion of platelets and cryoprecipitate (Post-CPB, diamonds), and immediately after admission to the cardiac intensive care unit (CICU, squares). Platelet counts (A) and ROTEM ExTEM (B) and PlTEM (C) values were determined immediately after blood samples were drawn. Results from patients who experienced normal (black symbols) vs. excessive (gray symbols) levels of bleeding were plotted separately. Each symbol represents the result for a single patient, bars denote means ± standard deviations, and dotted lines represent the normal ranges in healthy infants as described previously20 (n=44 for ROTEM ExTEM and PlTEM values; n = 41 for platelet counts - patients 2, 3, and 4 were excluded because of missing data). Generalized Estimating Equation (GEE) with maximum likelihood estimation method was used to model the variables over time accounting for bleeding status. Normal distribution with identity link function was used for comparisons. Note that platelet counts and ROTEM values did not differ significantly between patients who bled excessively vs. those who did not at any time point.