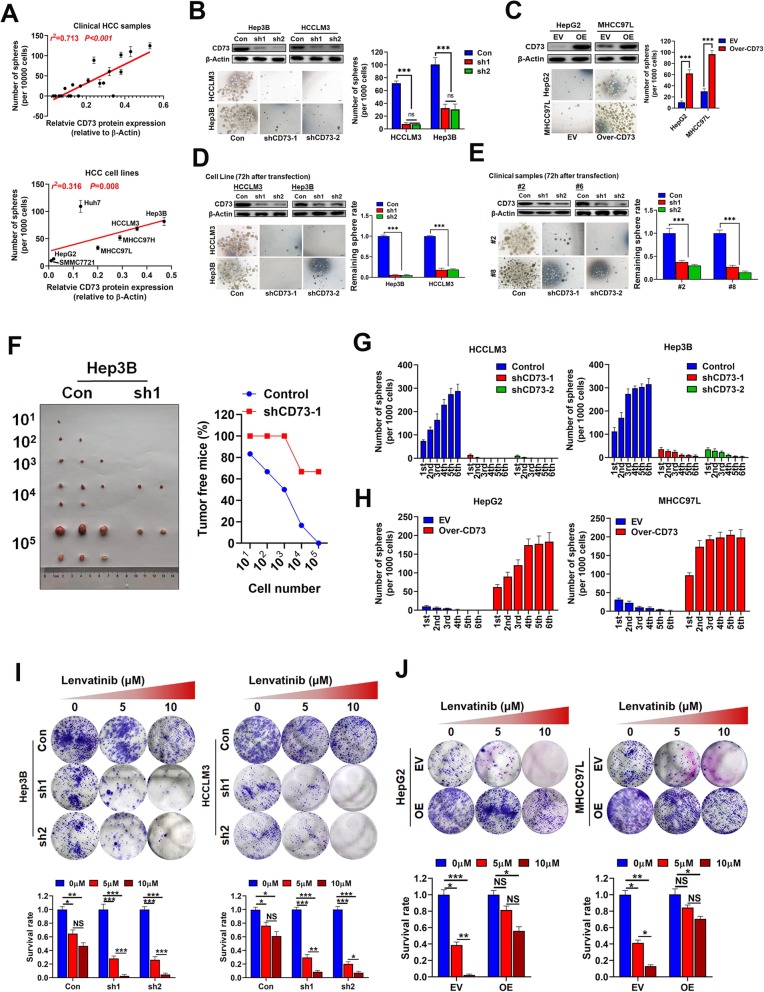
Fig. 1.
CD73 expression is essential for sustaining CSC traits. a Correlations between CD73 expression and number of spheres derived from clinical fresh HCC samples (upper) or HCC cell lines (lower). b Effects of CD73 knockdown on sphere-forming capacity in CD73-high HCC cell lines. CD73 knockdown efficiencies were validated by WB assays. c Effects of CD73 overexpression on sphere-forming capacity in CD73-low HCC cell lines. CD73 knockdown efficiencies were validated by WB assays. d CD73 knockdown interfered sphere-forming capacity in sphere cells derived from HCC cell lines. CD73 knockdown efficiencies were validated by WB assays. e CD73 knockdown interfered sphere-forming capacity in sphere cells derived from clinical fresh HCC samples. CD73 knockdown efficiencies were validated by WB assays. f Ratio of tumor-free mice after 12 weeks’ tumor formation after injection of indicated numbers of CD73-KD and control Hep3B cells. Images were shown in the left panel. g Sphere numbers of CD73-knocked down and control HCC cells according to serial sphere formation assays. h Sphere numbers of CD73-overexpressed and control HCC cells according to serial sphere formation assays. i Effects of CD73 knockdown on Lenvatinib resistance were evaluated by colony formation assays. Typical images were shown as upper panels. j Effects of CD73 overexpression on Lenvatinib resistance were evaluated by colony formation assays. Typical images were shown as upper panels. Throughout the figure, “*” indicated P < 0.05, “**” indicated P < 0.01, and “***” indicated P < 0.001 by two-tailed t test or Mann–Whitney test