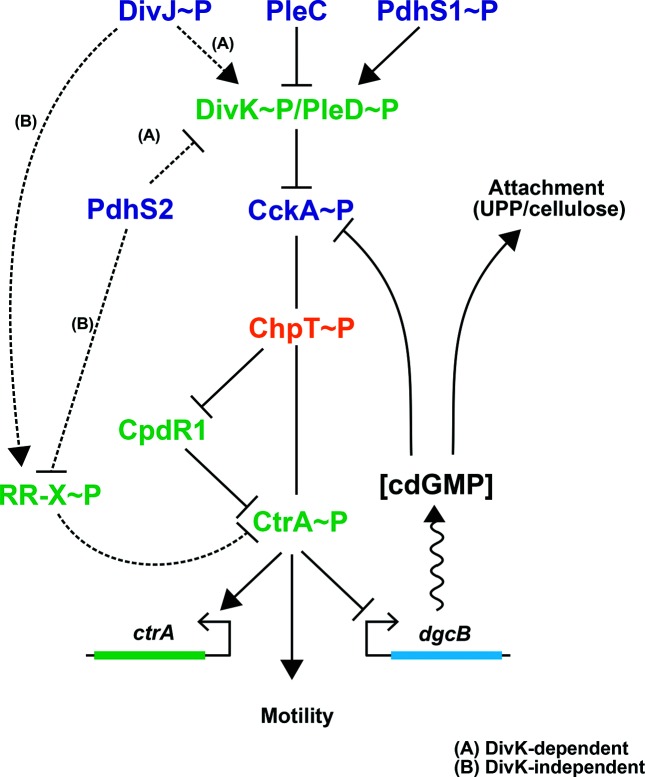
Fig. 7.
An alternative model for PdhS2 regulation of CtrA activity. Our data are consistent with PdhS2 intersecting the DivK–CtrA regulatory pathway at one of two points. Pathway A: canonical genetic model with PdhS2 interacting with DivK. The phosphorylation status of DivK then modulates CtrA activity through the CckA–ChpT–CtrA axis. Pathway B: DivK-independent model of CtrA regulation by PdhS2 through an unidentified response regulator, RR-X. Both routes to the regulation of CtrA activity ultimately affect the phosphorylation status of CtrA, affecting occupancy at CtrA-regulated promoters, and finally leading to inverse regulation of attachment (primarily through cdGMP pools) and separately motility. Regulatory proteins: blue text; histidine kinases; orange text, histidine phosphotransferase (Hpt), green text, response regulators. RR-X indicates a putative response regulator, yet to be identified.