Figure 4.
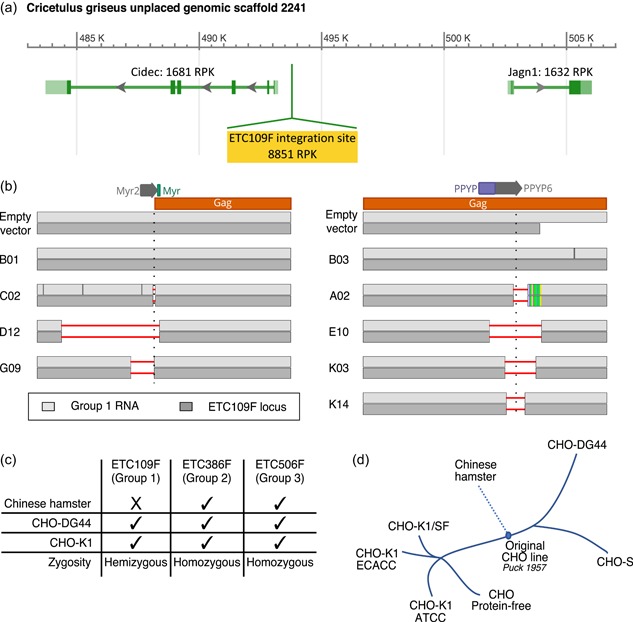
Identification of a unique functionally active group 1 type‐C endogenous retrovirus (ERV) locus and assessment of ERV conservation and zygosity in CHO cells and Chinese hamster genome. (a) Predicted group 1 type‐C ETC109F ERV integration site (highlighted in yellow) in the publicly available NCBI CHO‐K1 genome (NW_003613637.1 assembly). The genomic region surrounding the ERV integration site contains two annotated protein‐coding genes (Cidec, Jagn1) encoding the cell death‐inducing DFFA‐like effector protein involved in lipid metabolism and an endoplasmic reticulum protein involved in the early secretory pathway, respectively (Boztug et al., 2014; Puri et al., 2007). The predicted RNA expression levels for each gene in CHO‐K1 cells were estimated by RNA sequencing data and are expressed as Reads per Kilobase (RPK). (b) Sanger sequencing results of the Myr2 (left‐hand side) and PPYP6 (right‐hand side) sgRNA flanking regions of the indicated ERV‐mutated CHO cell clones. Sanger sequencing was performed on polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplicons obtained from reverse‐transcribed total cellular mRNA using group 1‐specific primers (in light gray), or from genomic DNA using primers specific to the ETC109F genomic locus (in the dark gray). Clones C02, D12, G09, A02, E10, K03, K14 contain deletions in the functionally active group 1 type‐C ERV locus (horizontal red lines), unlike the B01 and B03 control clones as well as the empty vector‐treated control cells. The predicted Myr2 and PPYP6 sgRNA‐mediated DNA cleavage sites are indicated with a vertical dotted line. (c) Genomic sequences of the expressed ETC109F, ETC386F, and ETC506F and flanking sequences were PCR amplified from CHO‐K1, CHO‐DG44, and Chinese hamster genomic DNA using primers specific to the left and right DNA borders or the ERV extremities, and the amplified DNA was analyzed by gel electrophoresis. Summary of the detection (tick) or absence (cross) of stably integrated ERVs into their corresponding genomic locus as well as their zygosity in the indicated genomes for the three expressed group 1, 2, or 3 ERVs (d) Description of the history of CHO cell lines, adapted from Lewis et al. (2013). CHO, Chinese hamster ovary [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
