Figure 2. Comparison of PAH composition between water and air samples.
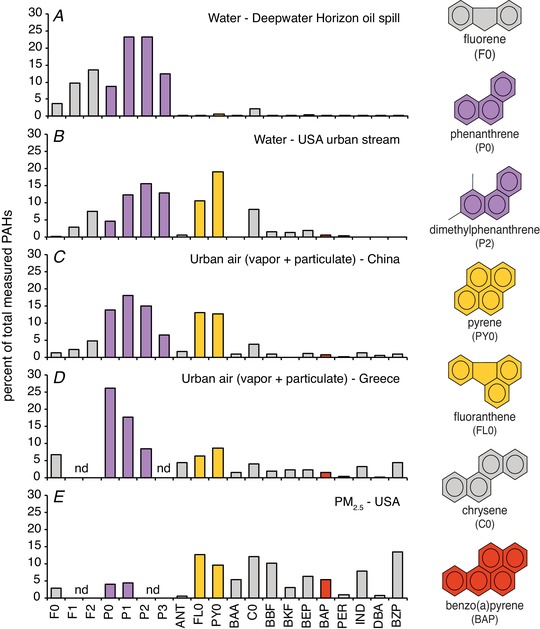
Composition profiles represent the percentage of the indicated PAHs normalized to the sum total of the measured set, with ring number and molecular weight increasing to the right. Parent non‐alkylated compounds are denoted with a 0 (e.g. F0, P0), while alkylated compounds (e.g. those with 1 or 2 additional methyl groups) are indicated by F1, F2, P1, P2, etc. Selected individual structures are shown on the right, with phenanthrene and its alkylated homologues indicated in purple, the 4‐ringed pyrogenic compounds indicated in gold (pyrene and fluoranthene), and the archetypal carcinogenic 5‐ringed PAH benzo(a)pyrene indicated in red. Five sample sources are shown. A, water from the area of the Gulf of Mexico impacted by the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill (Incardona et al. 2014); B, passive samplers placed in an urban stream in Seattle (USA) that receives large quantities of stormwater runoff from nearby roadways (Scholz et al. 2011; J. P. Incardona, unpublished); C, a total high volume air sample from Guangzhou (China) collected July 2001 by combined glass fibre filter (GFF) and polyurethane foam (PUF) plug (Bi et al. 2003); D, the mean of 16 total GFF/PUF samples collected between November 2000 and February 2002 in Heraklion (Greece) (Tsapakis & Stephanou, 2005); E, mean of quarterly samples collected over the year 2004 using a PM2.5 particle composition monitoring system at a heavily trafficked urban site in Atlanta, USA (Li et al. 2009). Abbreviations: F, fluorene; P, phenanthrene; ANT, anthracene; FL, fluoranthene; PY, pyrene; BAA, benz(a)anthracene; C, chrysene; BBF, benzo(b)fluoranthene; BKF, benzo(k)fluoranthene; BEP, benzo(e)pyrene; BAP, benzo(a)pyrene; PER, perylene; IND, indeno(123‐cd)pyrene; DBA, dibenzanthracene; BZP, benzo(ghi)perylene; nd, not determined.
