Figure 3. The effects of Phe on excitation contraction coupling.
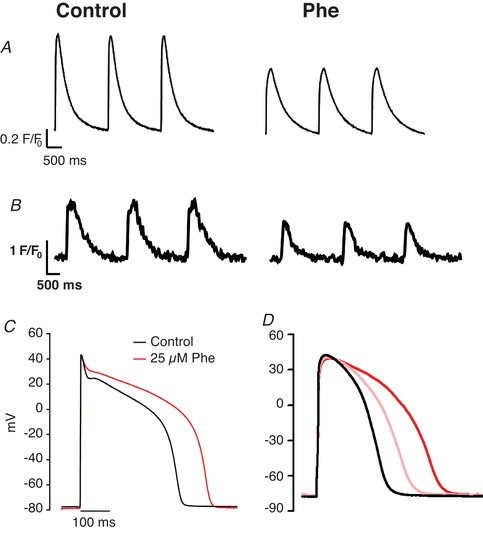
The effect of Phe on the intracellular Ca2+ transient in sheep ventricular myocytes (25 µM) (A) and fish (bluefin tuna, 5 µM) ventricular myocytes (B) loaded with Fluo‐4AM and stimulated to contract at 0.5 Hz. The effect of Phe on the ventricular AP during whole‐cell current clamp in sheep (C) and bluefin tuna (D) ventricular myocytes. The red lines in both traces show data recorded during exposure to 25 µM Phe. The pink line shows the effect of 5 µM Phe exposure in tuna. No discernible effects were seen at 5 µM in sheep (not shown). Tuna data are from Brette et al. 2017, with permission from Scientific Reports, and sheep data are unpublished data of C.R.M., S.N.K. and H.A.S. in myocytes supplied by the members of the laboratories of Dr K. Dibb and Prof. A. Trafford at the University of Manchester.
