Table 2. Selected optimization of the reaction conditions a .
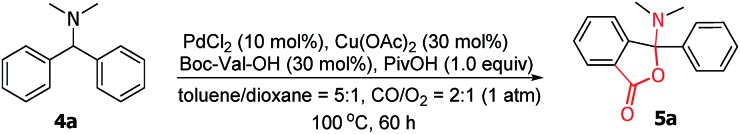
| ||
| Entry | Variation from standard conditions | Yield b (%) |
| 1 | None | 90(65) |
| 2 c | Without PdCl2 | ND e |
| 3 c | Without Cu(OAc)2 | ND |
| 4 c | Without PivOH | 42 |
| 5 c | AcOH instead of PivOH | 55 |
| 6 c | Cs2CO3 instead of PivOH | ND |
| 7 c | Pd(OA)2 instead of PdCl2 | Trace |
| 8 c | Pd(TFA)2 instead of PdCl2 | Trace |
| 9 c | CuCl2 instead of Cu(OAc)2 | Trace |
| 10 c | Cu(acace)2 instead of Cu(OAc)2 | 45 |
| 11 c | AgOAc as oxidant | Trace |
| 12 c | K2S2O8 as oxidant | Trace |
| 13 c | Toluene instead of mixed solvent | Trace |
| 14 c | i-PrOH instead of mixed solvent | Trace |
| 15 c | DMA instead of DMF | 35 |
| 16 | 110 °C instead of 100 °C | 82 |
| 17 | 90 °C instead of 100 °C | 55 |
| 18 | Boc–Phe–OH | 80 |
| 19 | Fomc–Val–OH | 72 |
| 20 | CO/O2 = 4 : 1 | 35 |
| 21 d | Add H2O (10 equiv.) | 17 |
a 4a (0.1 mmol), PdCl2 (10 mol%), Cu(OAc)2 (30 mol%), Boc–Val–OH (30 mol%), PivOH (1.0 equiv.), toluene/dioxane (5 : 1, 1.2 mL), V(CO)/V(O2) (2 : 1), 100 °C, 60 h.
bDetermined by GC-MS, isolated yield is given in the parenthesis.
cToluene/DMF (5 : 1, 1.2 mL), 120 °C.
d100 °C, 48 h.
eND = not determined.
