Figure 1.
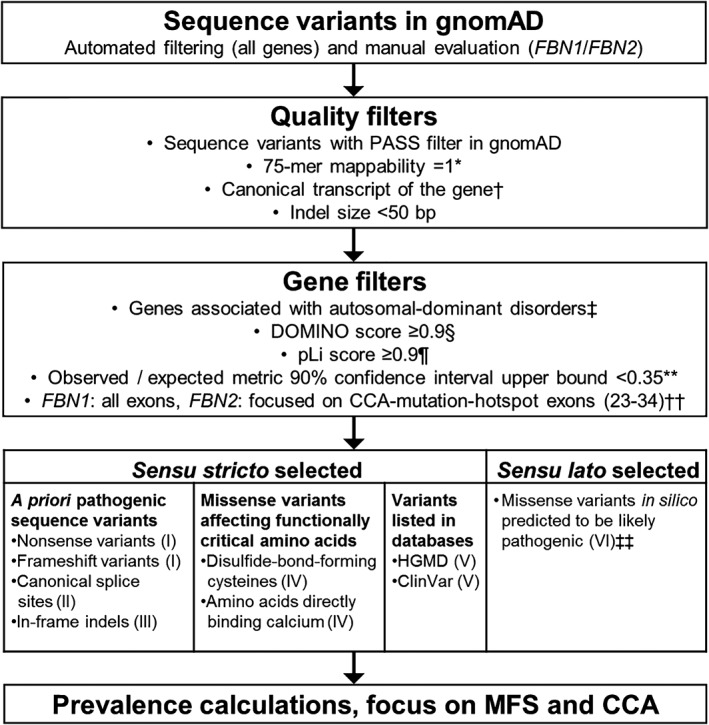
Overview of used workflow. Categories I and II were applied to all genes associated with autosomal‐dominant disorders in gnomAD, whereas categories III‐VI were only applied to FBN1 and FBN2. *,† Data obtained from the Tables “wgEncodeCrgMapabilityAlign75mer” (*) and “knownCanonical” (†) from the UCSC Table browser; http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTables. ‡ Data obtained from the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) dataset, 05.2018; http://omim.org. § According to Quinodoz et al. (2017).13 ¶ According to Lek et al. (2016).2 ** According to Karczewski et al. (2019).3 †† In FBN2 the prevalence calculation was limited to the CCA‐mutation‐hotspot region (exons 23‐34) for categories II‐VI, while for category I (nonsense and frameshift) all exons were considered. ‡‡ Sequence variants predicted “damaging” or “deleterious” by all six used in silico prediction tools (FATHMM, FATHMM‐MKL, MutationAssessor, MutationTaster, Polyphen2, SIFT; see also Supporting Information Table S1). CCA, congenital contractural arachnodactyly; gnomAD, Genome Aggregation Consortium; HGMD, Human Gene Mutation Database; indel, insertion/deletion; MFS, Marfan syndrome
