Figure 1.
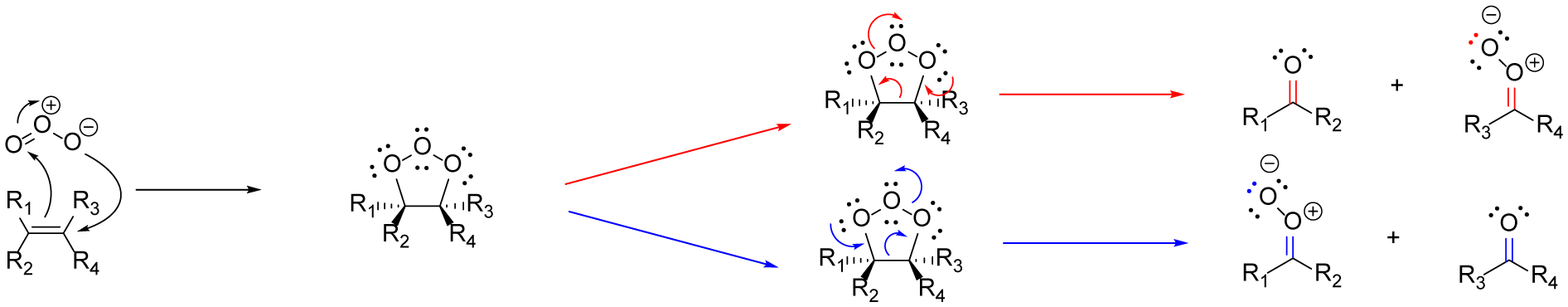
In ozonolysis carbon-carbon double bonds react with ozone via a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition. Two products are formed via the subsequent retro 1,3-diplolar cycloaddition, resulting in a ketone/aldehyde and a Criegee intermediate. The red arrows (top) and blue arrows (bottom) represent the two routes in which the molozonide can undergo the retro 1,3-diplolar cycloaddition.
