Table 1.
Key considerations for performing OzID-MS analysis.
| Questions | Reasoning |
|---|---|
| Why infuse salt adducts such as Na+? | The counter ion aids in OzID fragmentation. Essentially, the increased intensity of the ozonide ions leads to an increase in the ozonolysis efficiency.66 Other salts could be used, such as those that produce Li+ ions. |
| What differentiates the observation of aldehyde vs. ketone peaks? | This is based on the double bond substitution before OzID fragmentation occurs. If the carbon was di-substituted, then it becomes a ketone. Alternatively, if it was mono-substituted, it becomes an aldehyde. |
| What is the Criegee ion? | A Criegee ion is an ion with the same mass as the carbonyl oxide zwitterion (shown below). However, structurally it could undergo rearrangement to various isomeric forms, which may differ, depending on the compound, due to the high reactivity and rapid rearrangement of the intermediate. Examples could include carboxylic acids, vinyl hydroperoxides, dioxiranes, etc.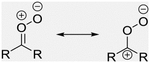
|
| Why is OzID-MS observed to occur from both sides of a molecule? | The counter ion (i.e. Na+) typically associates with oxygenation, and if two spots are available on either side of the metabolite, then both the theoretical carbonyl/Criegee ions pairs are observed. |
| Why are not all of the “potential” fragments produced for every double bond? | The distance between where the adduct associates and the double bond affects reactivity.37,67 |
| Why is [M+Na+16]+ a key observation? | This ion suggests that the metabolite has conjugated double bonds due to the formation of an epoxide.37,68 |
