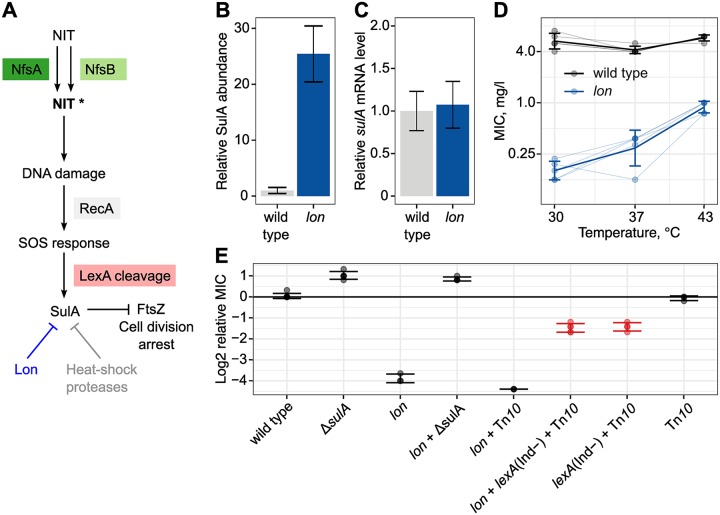
Fig 5. CS due to interference with the cellular drug response.
(A) Model for elevated susceptibility to NIT in a lon mutant due to induction of the SOS response. (B) Relative accumulation of SulA protein in the E. coli lon mutant in drug-free medium (mean ± SD, n = 2 biological replicates). (C) Transcription of sulA is unchanged in the lon mutant in drug-free medium (mean ± SD, n = 3 biological replicates). (D) Partial suppression of CS at high temperature (mean ± SD, n = 5 biological replicates). (E) Relative change of MIC compared to wild-type E. coli in mutants of the SOS response. CS is completely suppressed by deletion of sulA and partially suppressed by a noninducible allele of lexA (mean ± SD, n = 3–5 biological replicates). Numerical data are available in S1 Data. CS, collateral sensitivity; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration; NIT, nitrofurantoin; SulA, Suppressor of Lon.