Figure 5.
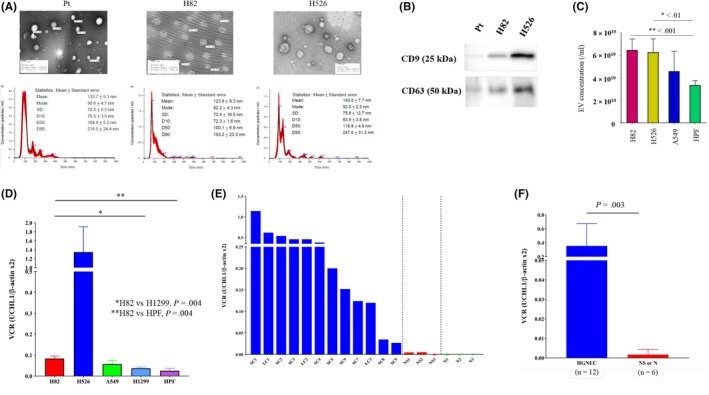
Characteristics of small cell lung cancer (SCLC)‐derived extracellular vesicles (EV) and quantification of UCHL1 levels in EV from SCLC patients and cell lines. A, Representative electron microscopic images and the results of nanoparticle characterization analysis providing the number of EV and the size distribution from the serum of an SCLC patient and two SCLC cell lines. B, Expression levels of CD9 and CD63 in EV from different cells were assayed by western blotting. C, Comparative analysis of EV production among the different cell lines. D, Comparative analysis of UCHL1 mRNA levels in cancer‐derived EV in vitro. SCLC cells, particularly H82 cells, showed higher UCHL1 levels in their EV compared with H1299 cells (P = 0.004) and HPF‐c cells (P = 0.004). E, UCHL1 mRNA levels in serum‐derived EV of p‐stage I‐II SCLC patients (n = 9), large cell neuroendocrine cancer (n = 3), non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (n = 3) and healthy donors (n = 3). LC, large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma; NS, non–small cell lung cancer; SC, small cell lung cancer. F, UCHL1 mRNA levels in serum‐derived EV of p‐stage I‐II high‐grade neuroendocrine cancer patients (n = 12) was significantly higher than those of p‐stage I‐II NSCLC or healthy donors (n = 6, P = 0.393)
