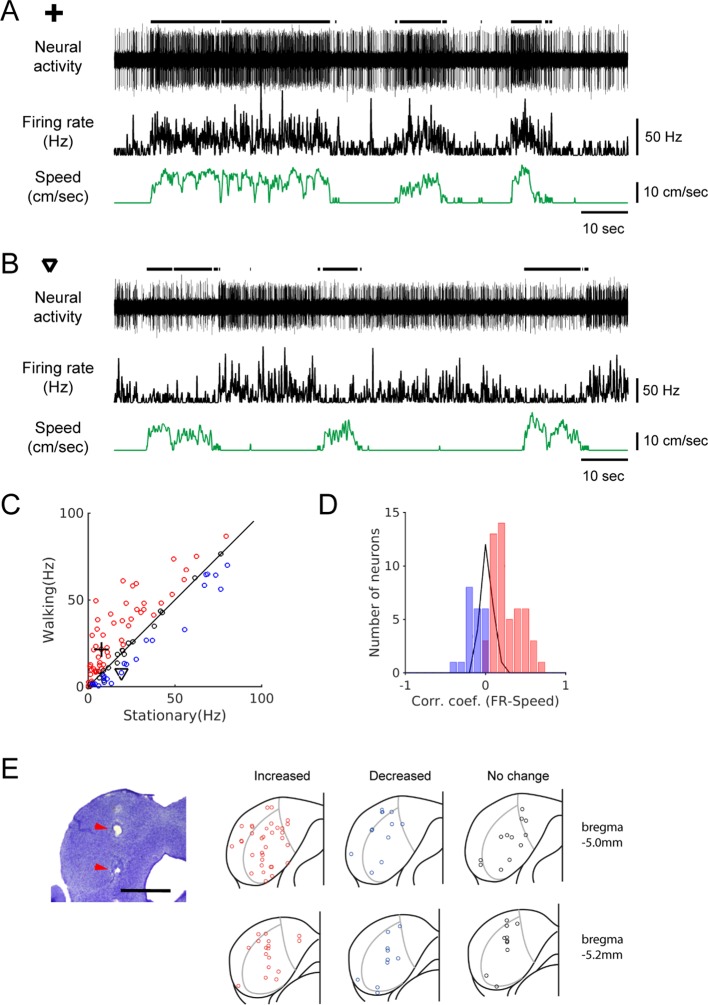
Figure 1. Spontaneous activity of IC neurons is modulated by locomotion.
(A-B) Example recordings of spontaneous activity in IC neurons. During walking periods, the neuron in A increased firing (from 7.6 Hz to 21.6 Hz), whereas the neuron in B decreased firing (from 19.1 Hz to 8.2 Hz). In both cases, the smoothed firing rates (black middle traces) exhibit significant correlations with the speed of the treadmill (green traces) (A: r = 0.59; B: r = −0.24). Thick black lines above the neural records indicate walking periods. (C) Population plot comparing average spontaneous firing rates between stationary and walking conditions (n = 96 neurons). Red circles: increased, blue: decreased, black: no significant change in firing. Values for the example neurons in A (cross) and B (triangle) are also shown. (D) Histogram of correlation coefficients between smoothed firing rate and speed (color code as in C). (E) Photomicrograph of a Nissl section with lesion sites marked with red arrow heads (scale bar = 1 mm), and reconstructed recording locations are shown in two transverse sections (5.0 and 5.2 mm posterior to the bregma, respectively). Color code as in C.