Figure 1.
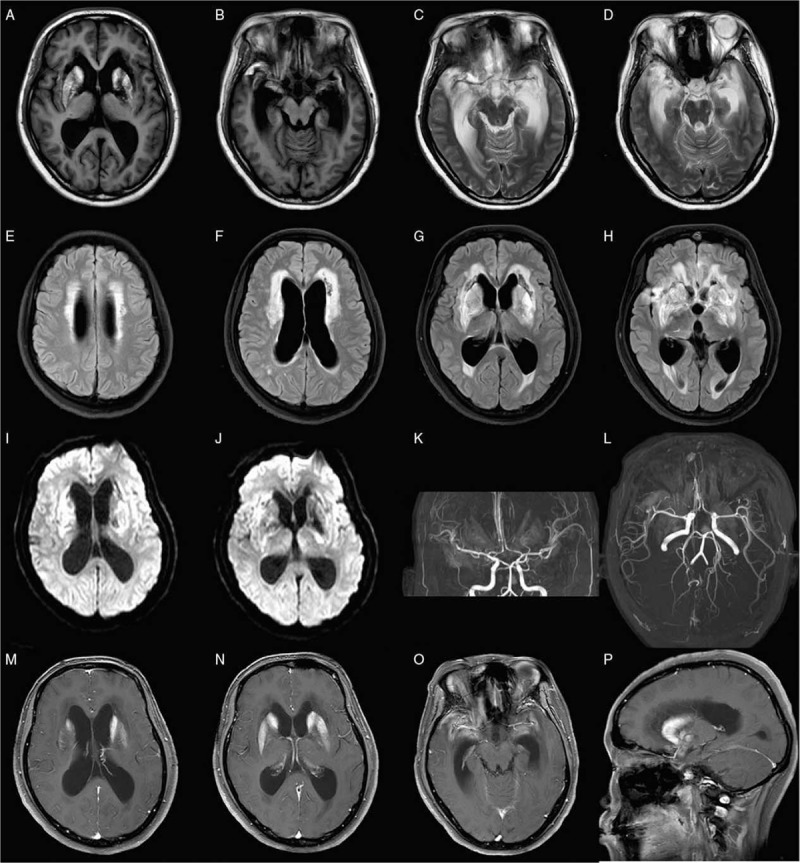
Cranial MRI images of the patient. (A and B) T1 images revealed hemorrhage of bilateral basal ganglia and temporal lobes. (C and D) Cranial MRI of T2, (E–H) FLAIR, and (I and J) DWI images revealed multiple abnormal signals in the bilateral basal ganglia and bilateral paraventricular and frontotemporal lobes, complicated with acute cerebral ischemia, infarction hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, and interstitial brain edema. Magnetic resonance angiography showed multiple intracranial vascular lumen thinning, wall thinning, and roughness. T1 images with contrast revealed abnormal enhancement of meninges (M–P). DWI: Diffused weighted image; FLAIR: Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; MRI: Magnetic resonance image.
