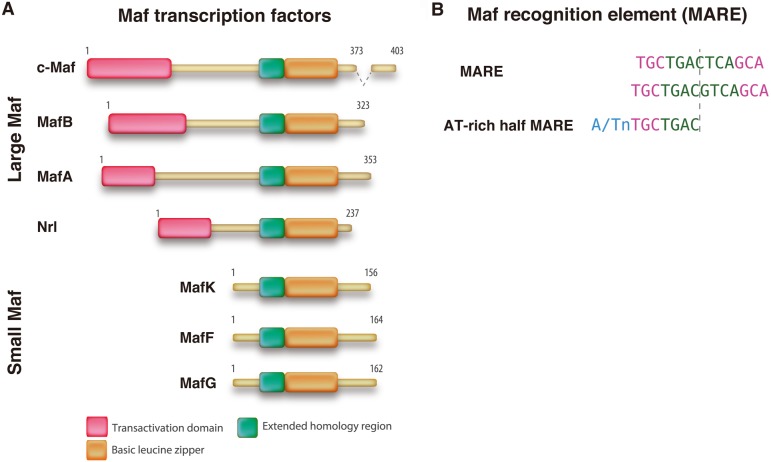
Fig. 1.
Structural features of Maf proteins. A. Schematic diagrams of four large Maf and three small Maf protein structures. Their amino acid lengths are indicated on the right side. The small Maf proteins are essentially composed of a carboxy-terminal basic leucine zipper (b-Zip) domain and a DNA-binding domain, whereas the large Maf proteins contain an additional transactivation domain. B. Maf proteins bind as homodimers to two types of target sequences, the classical Maf recognition element (MARE) site and the 5’-AT-rich MARE half-site.