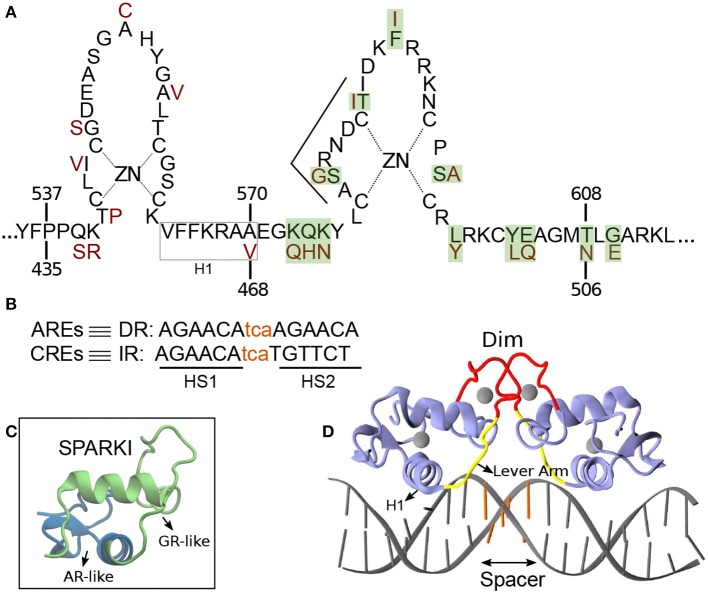
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic overview of the DNA binding domain (DBD) sequences in the androgen receptor (AR) and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) protein with corresponding residue numbers above and below, respectively. The amino acids colored in dark red are those elements of the GR-DBD that differ from the AR-DBD sequence. The other amino acids are the same in the AR- and GR-DBD. The amino acids shown with green shadow are those elements in AR that are replaced with residues from GR in order to make Sparki (Schauwaers et al., 2007). (B) DNA sequences for direct (DR) and inverted repeats (IR). The non-capital letters are the spacer base-pairs, colored in orange. (C) Schematic 3D structure of one monomer of Sparki-DBD, regions colored in green and blue are those subdomains that are GR- and AR-like, respectively. (D) The 3D structure of the GR- DBD/DNA complex (pdb ID: 1R4R). A similar structure exists for the AR-DBD/DNA complex (pdb ID: 1R4I). The lever arm and dimerization domain (Dim) are shown in yellow and red, respectively. The spacer region of the DNA is colored with orange.