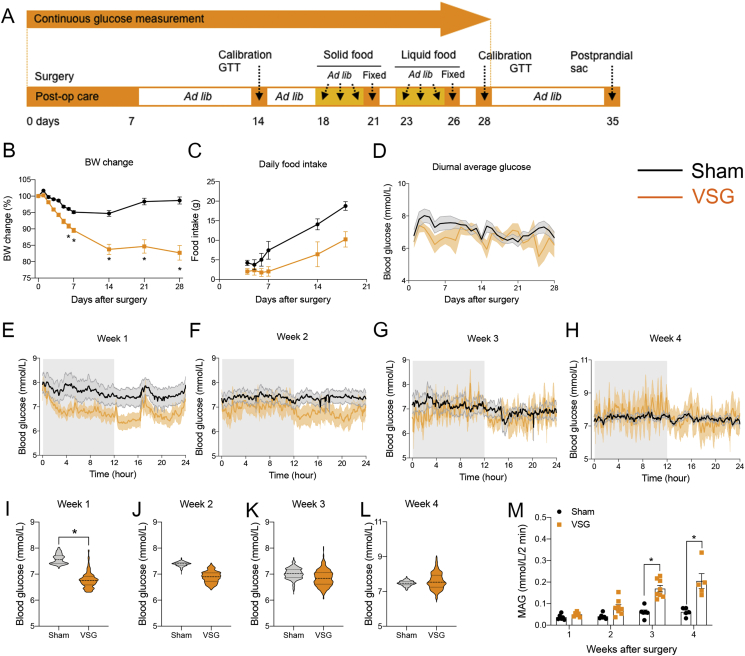
Figure 1.
CGM demonstrates glycemic variability after VSG in rat. (A) Schematic experimental timeline during CGM after surgery. (B–D) Body weight changes (B), daily food intake (C), and average glucose levels (D) across the 28 days after surgery. Mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 for sham vs. VSG (mixed-effects model; time × surgery). (E–H) Diurnal average glucose levels during the first (E), second (F), third (G), and fourth (H) weeks after surgery. The shaded gray area reflects glucose levels during the dark cycle. Mean ± SEM. (I–L) Violin plots represents the median, quartiles, minimum, maximum, and distribution of diurnal glucose levels during the first (I), second (J), third (K), and fourth (L) weeks after surgery. *P < 0.05. (M) Mean absolute glucose (MAG) after surgery. Mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 (mixed-effects model; time × surgery). All data were obtained from n = 6 sham and n = 8 VSG animals, except for the observations from the fourth week, which included n = 4 sham and n = 5 VSG animals.